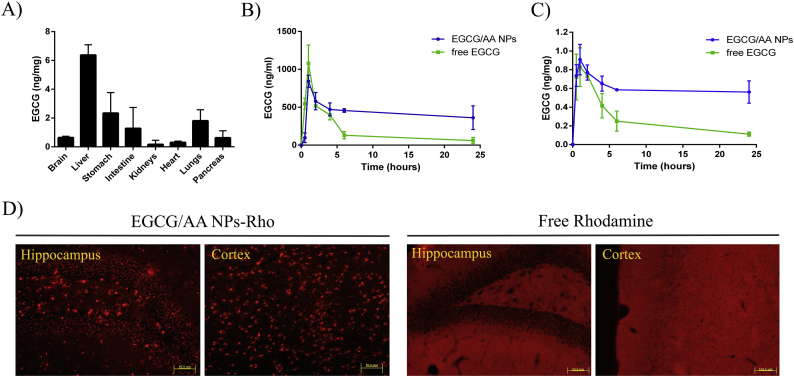
Fig. 3.
In vivo biodistribution and pharmacokinetics of EGCG/AA NPs. 3 months-old C57BL/6 WT mice were treated with a single oral dose of EGCG/AA NPs and EGCG/AA NPs-Rho 40 mg/kg. (A) Histograms show biodistribution of EGCG in brain, liver, stomach, intestine, kidneys, heart, lungs and pancreas of mice after 24 h of EGCG/AA NPs administration. Data expressed as EGCG amount per mg of tissue. Mean administered volume of EGCG/AA NPs was 448 μl (1.120 mg). Mean brain EGCG concentration was 0.6 ng/ml. With mean brain weight of 470 mg this represented 0.025% of administered EGCG. (B) Plasma and (C) brain pharmacokinetic profile of EGCG following single oral dose administration of free EGCG or EGCG/AA NPs (40 mg/kg). Data expressed as EGCG amount per ml of plasma and EGCG amount per mg of tissue, respectively. (D) Rhodamine detection in the dentatus gyrus of the hippocampus and the cortex of mice treated with EGCG/AA NPs-Rho (40 mg/kg) or free Rhodamine (2.7 mg/kg). Scale bar 50 μm.