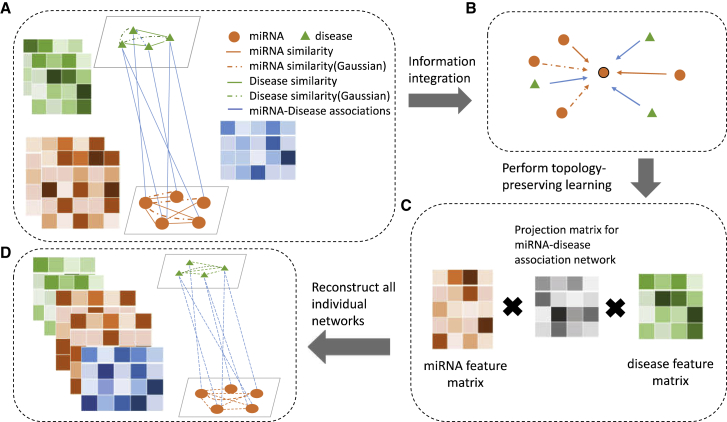
Figure 3.
Flowchart of NNMDA
(A) NNMDA uses several individual miRNA-related or disease-related networks to construct a heterogeneous network (details of the used datasets are introduced in Materials and Methods). In a heterogeneous network, different types of nodes are connected by distinct types of edges. Two nodes can be connected by more than one edge (e.g., the solid link between diseases representing disease functional similarity and the chain line between them representing disease Gaussian similarity). (B) Each node adopts a neighborhood information aggregation operation to extract information from the neighborhood. Each arrow represents a specific aggregation function with respect to a specific edge type. Each node then updates its feature representation by integrating its current representation with the aggregated information. (C) NNMDA learns the topology-preserving node features that are useful for miRNA-disease interaction prediction by enforcing the node features to reconstruct the original individual networks. (D) Reconstruction of all individual matrices.