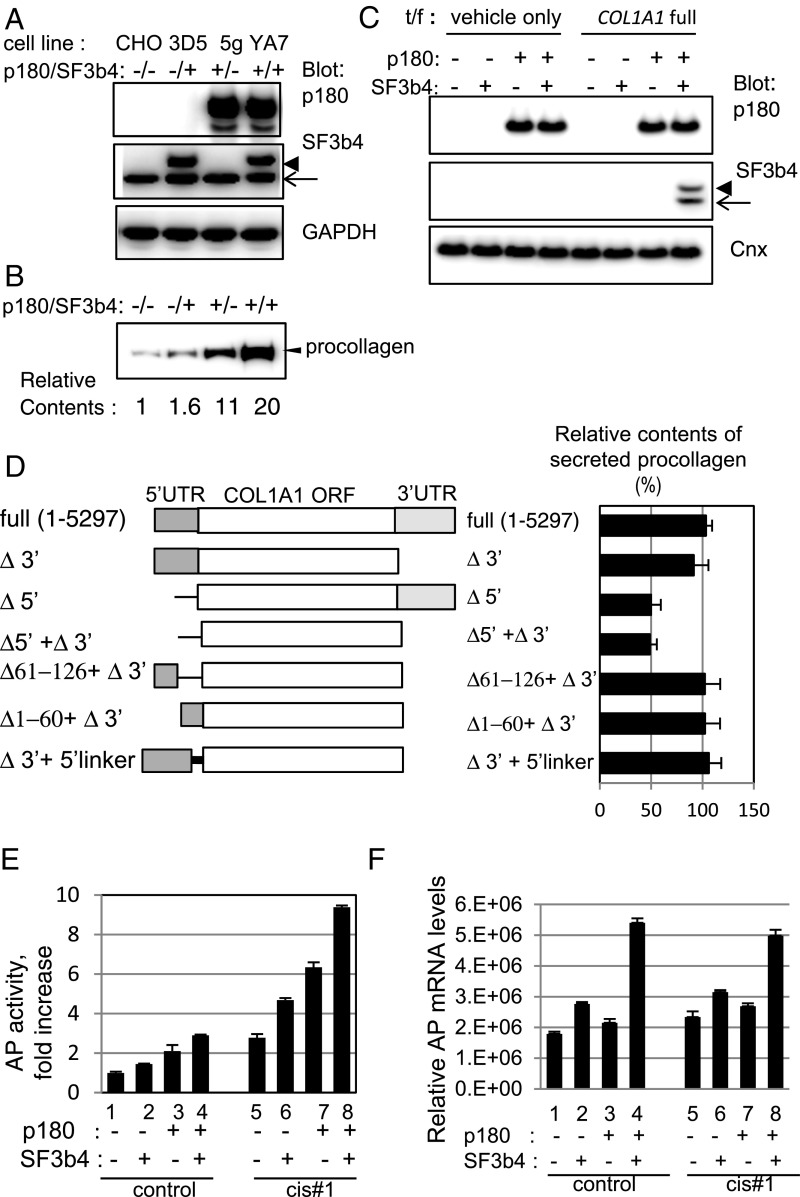
Fig. 3.
The 5′ UTR sequence in COL1A1 mRNA is important for enhanced translation in a stable cell line coexpressing p180 and SF3b4. (A) Protein expression levels in established CHO stable cell lines expressing p180 (clone 5g), SF3b4 (clone 3D5), or both proteins (clone YA7) were analyzed. p180 was not detected in control CHO and 3D5 cells. An arrow indicates positions for endogenous SF3b4, whereas an arrowhead indicates that of recombinant myc-tagged SF3b4; the same applies hereafter. (B) The four indicated cell lines were transfected with an expression vector encoding full-length procollagen cDNA of the COL1A1 gene. Secretion levels of procollagen were analyzed by Western blotting. Relative amounts estimated by densitometric scanning are shown below the image. (C) Membrane fractions were prepared from cells transfected with a vector encoding full-length COL1A1 or empty vector as indicated, and the p180 and SF3b4 levels in each fraction were compared. (D) Schematic structures of full-length and truncated mutants of human COL1A1 cDNA (Left). A mutant with a 13-nt (aagcttcgaattc) linker inserted at the initiation codon (5′-linker) was used to prevent stem–loop formation (21). Bar graphs (Right) represent relative procollagen secretion levels (%) in 3-d culture media from YA7 cells. (E) Cells were transfected with control reporter plasmid (lanes 1–4) or reporter plasmid containing cis#1 upstream of the ORF encoding AP (lanes 5–8). Relative secreted AP activity is shown (vs. the value in lane 1, set as 1). (F) Relative AP mRNA levels of the membrane fractions of the transfected cells are depicted.