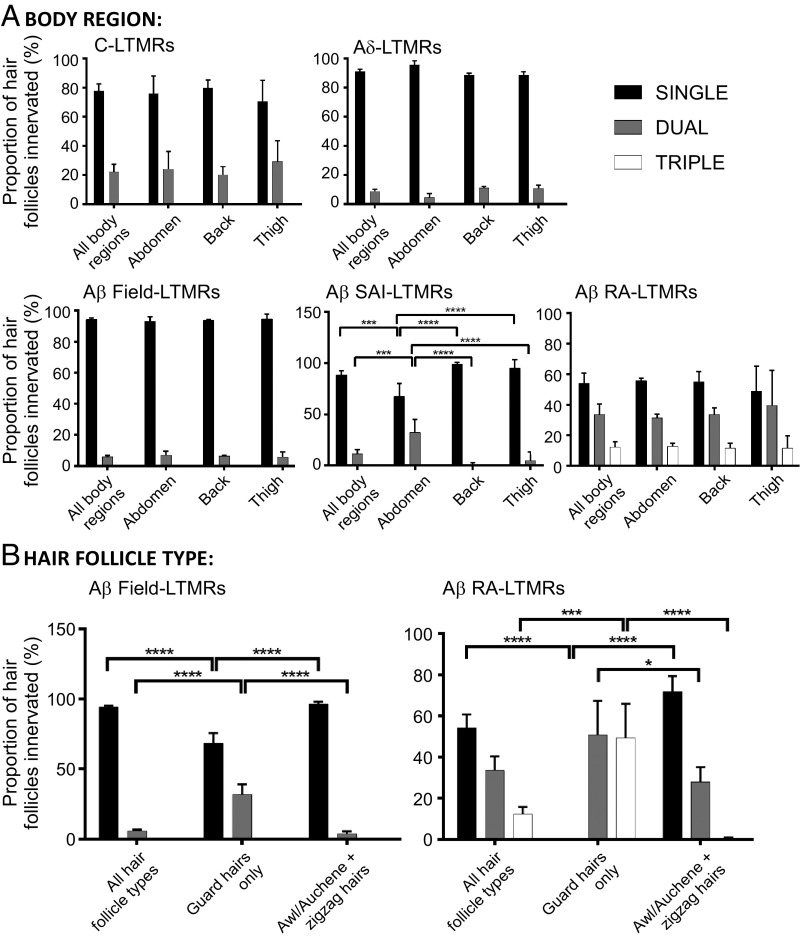
Fig. 3.
LTMR peripheral receptive field overlap patterns differ according to body region or hair follicle type. Quantifications of relative peripheral overlap within specific LTMR subpopulations according to (A) body region or (B) hair follicle type. Of the total hair follicles innervated by each LTMR subtype, bars indicate the relative fraction that receive single (black), dual (gray), or triple (white) innervation from that subtype. C-LTMRs (0.07 mg tamoxifen at P16 to TH2A-CreER;Ai3/Ai9, n = 3 animals), Aδ-LTMRs (3 mg at E12.5 to TrkBCreER;Ai3/Ai9, n = 4 animals), Aβ Field-LTMRs (2 mg at E16.5 to TrkCCreER;Ai3/Ai9, n = 3 animals), Aβ SAI-LTMRs (2 mg at E12.5 to TrkCCreER;Ai3/Ai9, n = 3 animals), and Aβ RA-LTMRs (2 mg at E11.5 to E12.5 to RetCreERAi3/Ai9, n = 3 animals). For comparisons between innervation patterns according to body region or hair follicle type, statistical significance is denoted above bars by brackets. For Aβ SAI-LTMRs: Two-way ANOVA: P < 0.0001, F(6, 30) = 18.99. For Aβ Field-LTMRs: two-way ANOVA: P < 0.0001, F(4, 21) = 72.79. For Aβ RA-LTMRs: two-way ANOVA: P < 0.0001, F(4, 18) = 38.97. Post hoc Tukey’s test: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.0005, ****P < 0.0001.