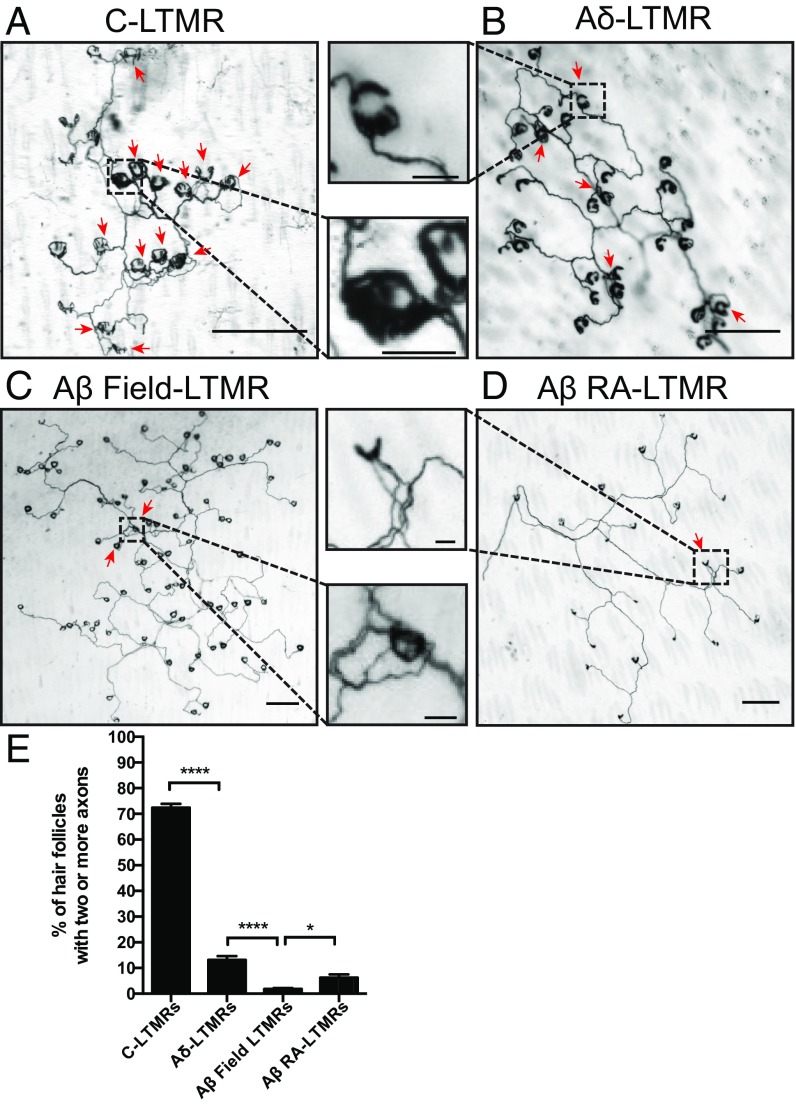
Fig. 4.
Individual LTMR peripheral axonal branches innervating hair follicles are largely nonoverlapping, with the exception of C-LTMRs. Representative images from hairy skin whole-mount AP staining of sparsely labeled (A) C-LTMRs, (B) Aδ-LTMRs, (C) Aβ Field-LTMRs, and (D) Aβ RA-LTMRs. (Scale bars, 200 μm; Insets, 30 μm.) (E) Quantifications of isoneuronal axonal overlap within individual LTMR receptive fields. C-LTMRs [1 mg at P12 to TH2A-CreER;Brn3af(AP); n = 32 neurons], Aδ-LTMRs [0.001 mg at P10 to TrkBCreER;Brn3af(AP); n = 26 neurons], Aβ Field-LTMRs [0.01 mg at P8 to TrkCCreER;Brn3af(AP); n = 26 neurons], Aβ RA-LTMRs [0.03 mg at E11.5 to RetCreER; Brn3af(AP); n = 35 neurons]. Bars represent the relative fraction of innervated hair follicles that receive innervation by multiple axonal branches of individual neurons for each LTMR subtype. Red arrows indicate hair follicles that are innervated by multiple axons. One-way ANOVA: *P < 0.05, ****P < 0.0001.