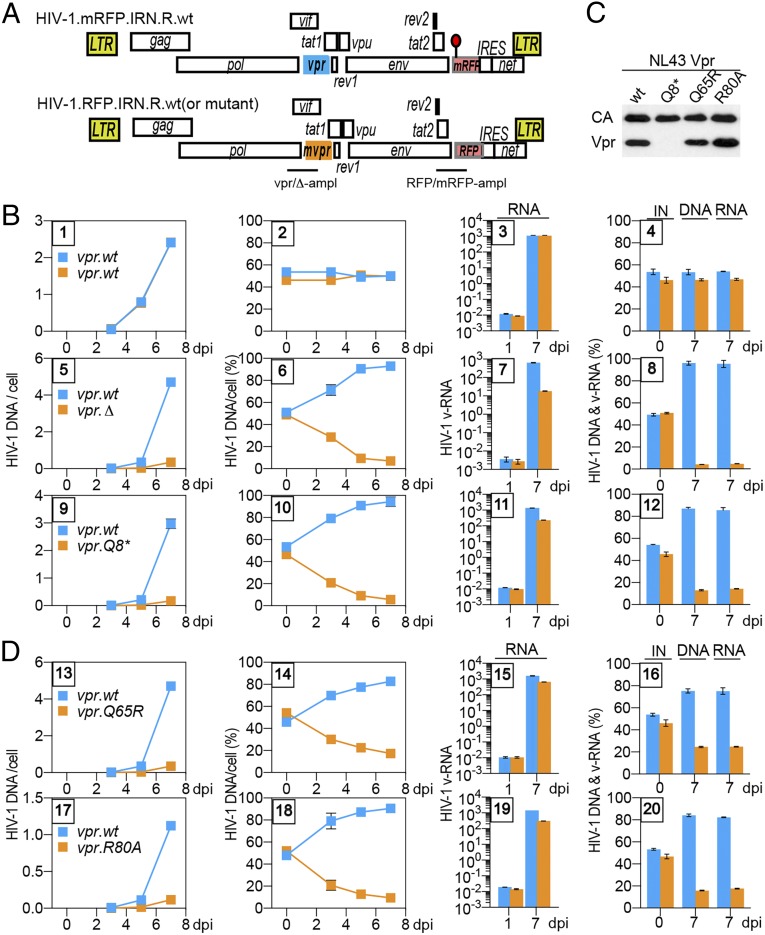
Fig. 1.
Vpr promotes HIV-1 replication in CEM.SS T cells. (A) Schematic representation of HIV-1.mRFP.vpr and HIV-1.RFP.vpr reporter constructs used in the PRCA. ORFs are shown as rectangles. The viruses are isogenic, except for an array of silent mutations in the RFP gene, indicated by a red lollipop, which provides unique primer annealing sites in the wt RFP and its mutant (mRFP) that allow their quantification by qPCR in coinfection assays. In some experiments, mutations were introduced into the vpr gene (mvpr) of the HIV-1.RFP construct. For the mvpr constructs, another set of primers, distinguishing between the vpr.wt and vpr.Δ alleles, was used to quantify viruses carrying those alleles. The locations of the vpr.wt, the deleted vpr.Δ amplicons (vpr-ampl), and the RFP and mRFP amplicons (RFP-ampl) are indicated. (B) PRCA reveals a positive effect of HIV-1 vpr on HIV-1 replication in CEM.SS T cells. CEM.SS T cells were infected with a normalized mixture, at 1:1 ratio, of HIV-1.mRFP.vpr.wt and HIV-1.RFP.vpr.wt (panels 1–4), HIV-1.mRFP.vpr.wt and HIV-1.RFP.vpr.Δ (panels 5–8), or HIV-1.mRFP.vpr.wt and HIV-1.RFP.vpr.Q8* (panels 9–12), at an moi of 0.006–0.02. The infected cultures were sampled 3, 5, and 7 dpi, and cell-associated HIV-1 DNA, as well as cell-free HIV-1 RNA, for each of the competing viruses was quantified by qRT-PCR, using mRFP and RFP amplicons and, in some experiments, also using vpr.wt and vpr.Δ amplicons (SI Appendix, Fig. S1). The number of copies per cell of cell-associated HIV-1 DNA from each of the competing viruses is shown in panels 1, 5, and 9, with the relative percentages shown in panels 2, 6, and 10. Quantification of cell-free viral RNA in culture medium on 1 dpi and 7 dpi is shown in panels 3, 7, and 11. Percentages of the competing viruses in the initial infecting mixture (IN) of cell-associated DNA and cell-free RNA at 7 dpi are shown in panels 4, 8, and 12. The cell-associated HIV-1 DNA data (two leftmost panels) and the virion-associated HIV-1 RNA data (two rightmost panels) are from different experiments. The data are representative of three independent experiments. (C) Virion incorporation of mutant HIV-1 Vpr proteins. Concentrated, normalized HIV-1.mRFP.R viruses with wt or mutated vpr gene were analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies reacting with p24 capsid or HIV-1 Vpr. (D) Vpr functions mediated via Q65 and R80 account for the positive effect of Vpr on viral fitness. PRCA was performed as described above with the HIV-1.mRFP.vpr.wt and HIV-1.RFP.vpr.Q65R mixture (panels 13–16) or the HIV-1.mRFP.vpr.wt and HIV-1.RFP.vpr.R80A mixture (panels 17–20).