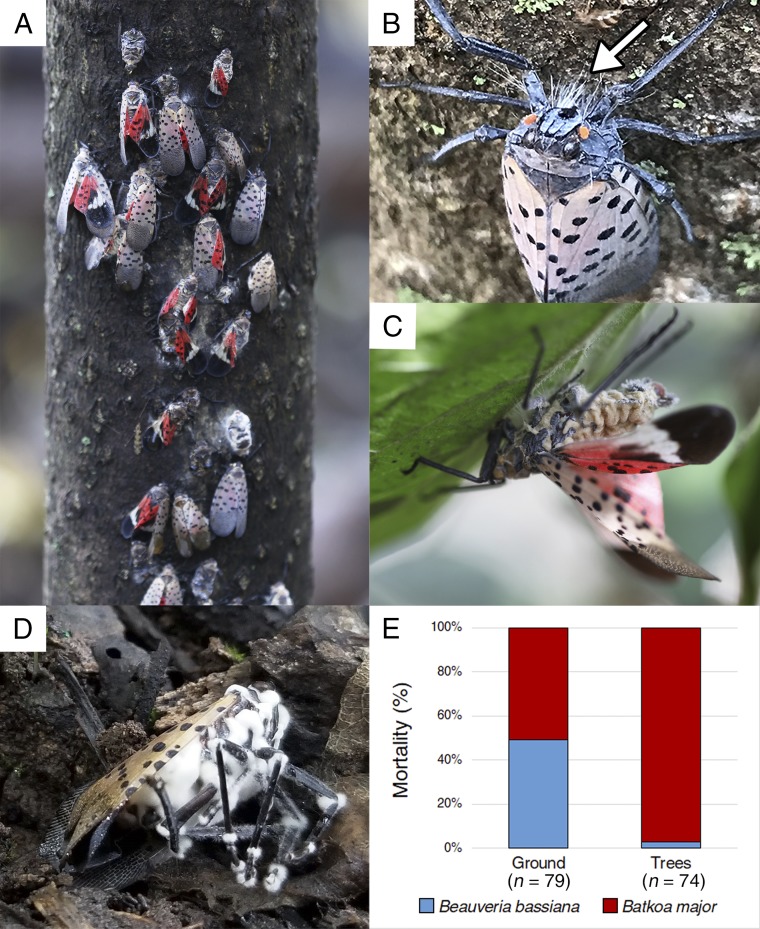
Fig. 1.
Two fungal pathogens causing a coepizootic in an L. delicatula population. (A) L. delicatula during the epizootic: only one of these adults was alive and the remainder had been killed by B. major. A similar degree of mortality was observed on trees throughout the site. (B) Rhizoids from B. major (arrow) attaching a dead adult to a tree. Image courtesy of Kelly Murman (photographer). (C) Adult cadaver with wings and legs extended outward as B. major conidia are released from the abdomen. (D) Adult killed by B. bassiana. (E) Percent L. delicatula killed by either pathogen on the trees or surrounding ground. Sample size is below each bar.