Figure 2. AR declines more rapidly for patients with nfvPPA over a 1-year period.
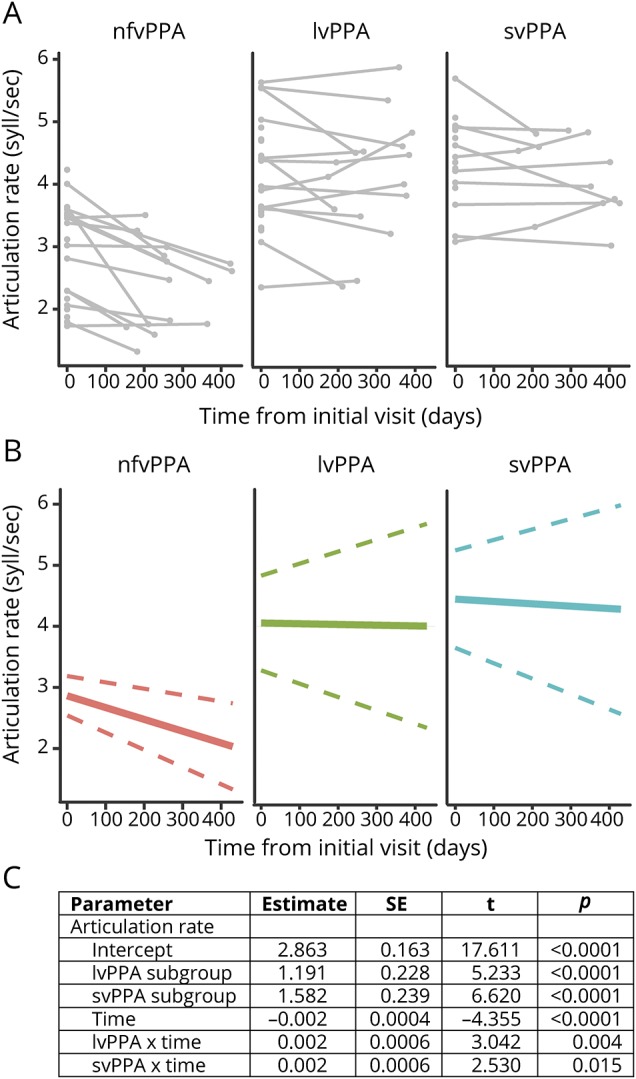
Longitudinal data collected for a subset (n = 39) of patients with primary progressive aphasia (PPA) reveal a significantly more rapid decline in articulation rate (AR) for patients with nonfluent variant PPA (nfvPPA) compared to those with logopenic variant PPA (lvPPA) and semantic variant PPA (svPPA). (A) Individual data points at baseline and (when available) the follow-up visit separated by subgroup. Connected lines show individual trends. (B) Subgroup trends in AR as a function of time based on linear mixed-effects (LME) model output. Solid line shows mean group slope; dashed line shows 95% confidence interval of mean group slope. (C) LME results demonstrate significant main effects of subgroup, time, and time × subgroup interaction. SE = standard error.
