Figure 8.
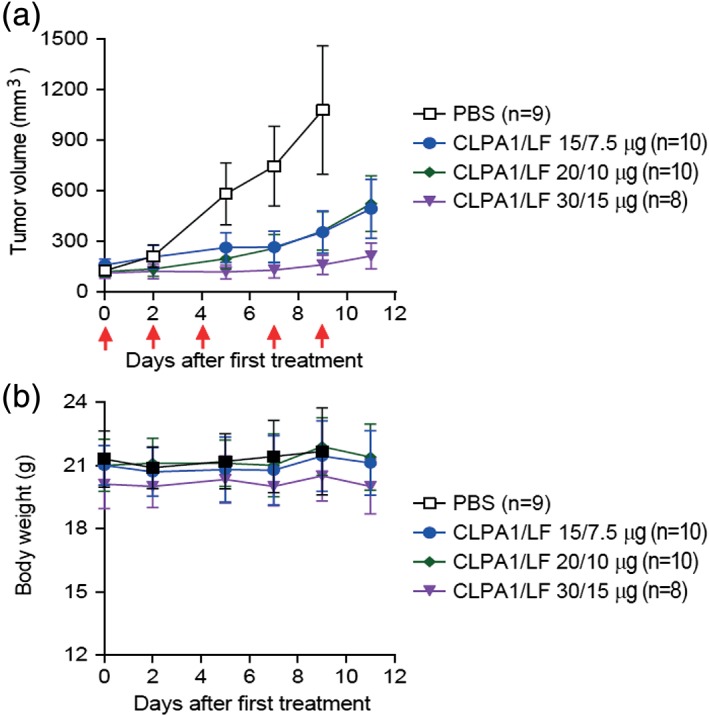
CLPA has potent antitumor activity when administered systemically to mice. C57BL/6J mice were inoculated intradermally with syngeneic LLC Lewis lung carcinoma cells. When tumors had formed, the mice were randomized into four groups (each of 8–10 mice, as indicated) that were treated with five systemic administrations (red arrows) of either PBS (open black boxes) or CLPA1 + LF at the doses shown. (a) Tumor volume and (b) body weight, as determined prior to each injection. Tumor volumes, mean ± SE; body weights, mean ± SD. One‐way ANOVA analysis (two‐tailed) for tumor size differences: PBS versus all other groups, P < 0.01; CLPA1/LF (15 μg/7.5 μg) and CLPA1/LF (20 μg/10 μg) versus CLPA1/LF (30 μg/15 μg), P < 0.05. At Day 9, the mice in the PBS group were terminated, whereas no mice were lost in any of the treated groups.
