Figure 2.
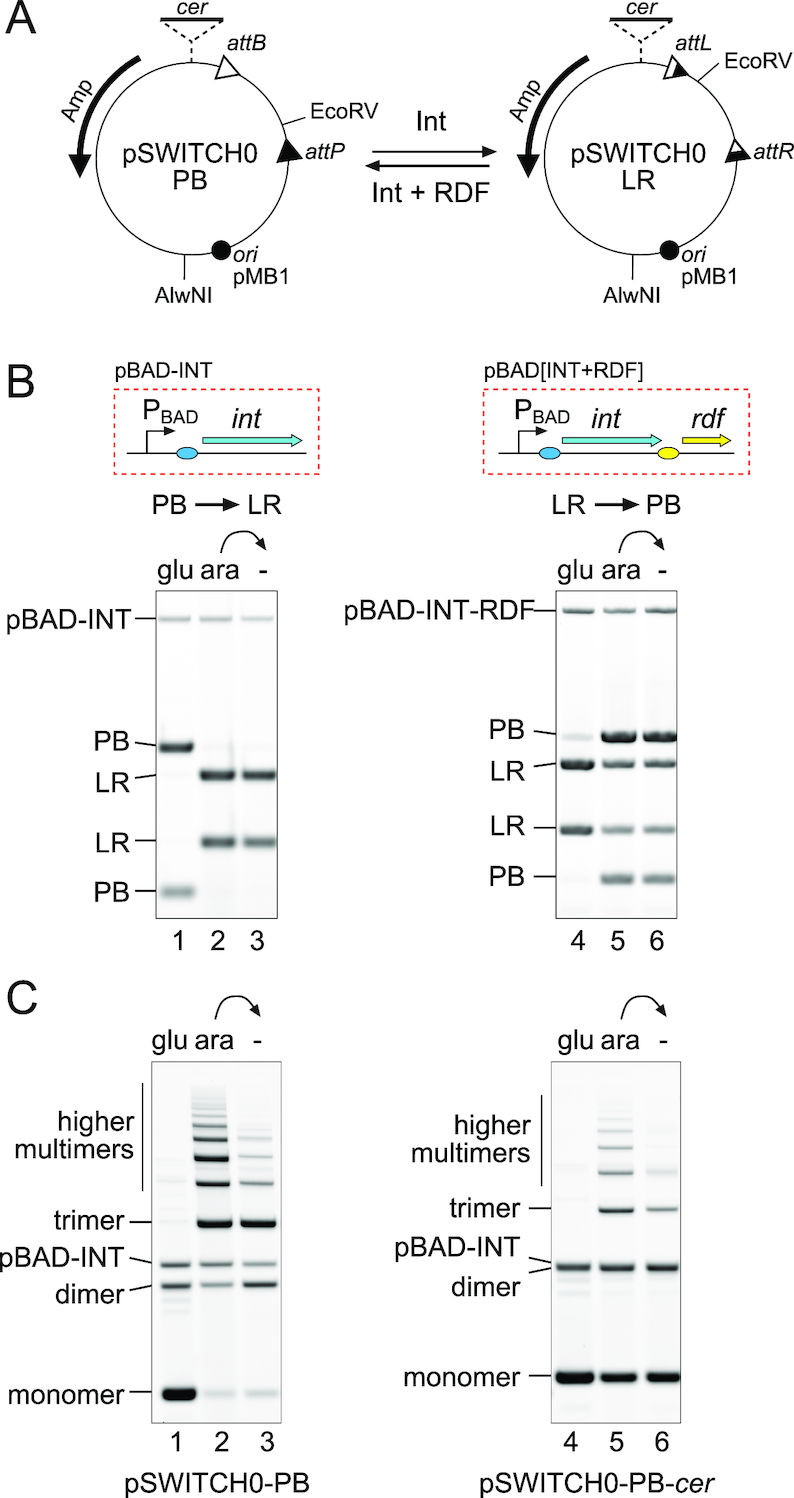
Directional recombination on high copy-number plasmids. (A) Diagrams of high copy-number switch plasmids containing an invertible DNA segment in the PB (pSWITCH0-PB) or the LR state (pSWITCH0-LR). (B) These plasmids were introduced into Escherichia coli DS941 together with a plasmid expressing either φC31 integrase (pBAD-INT; left panel) or integrase with its RDF (pBAD[INT+RDF]; right panel) from the arabinose-inducible PBAD promoter. Cells were grown overnight in LB containing 0.2% glucose to repress expression from PBAD (lanes 1 and 4), or overnight with 0.2% arabinose to induce expression from PBAD (lanes 2 and 5). The cells that had been grown overnight with arabinose were subsequently diluted 1:1000 and grown overnight again without inducer (lanes 3 and 6). Plasmid DNA was purified and cut with AlwNI and EcoRV. (C) The left panel (lanes 1–3) shows the same samples as shown in the left panel of (B), run on an agarose gel without prior restriction digestion, to reveal plasmid multimers produced by intermolecular recombination. A multimer resolution site (cer) was added to pSWITCH0 at the position indicated in (A) (dotted lines) to create pSWITCH0-cer. DS941 containing pSWITCH0-PB-cer and pBAD-INT was grown with or without arabinose induction as in (B) and analysed by gel electrophoresis without restriction digestion (lanes 4–6).
