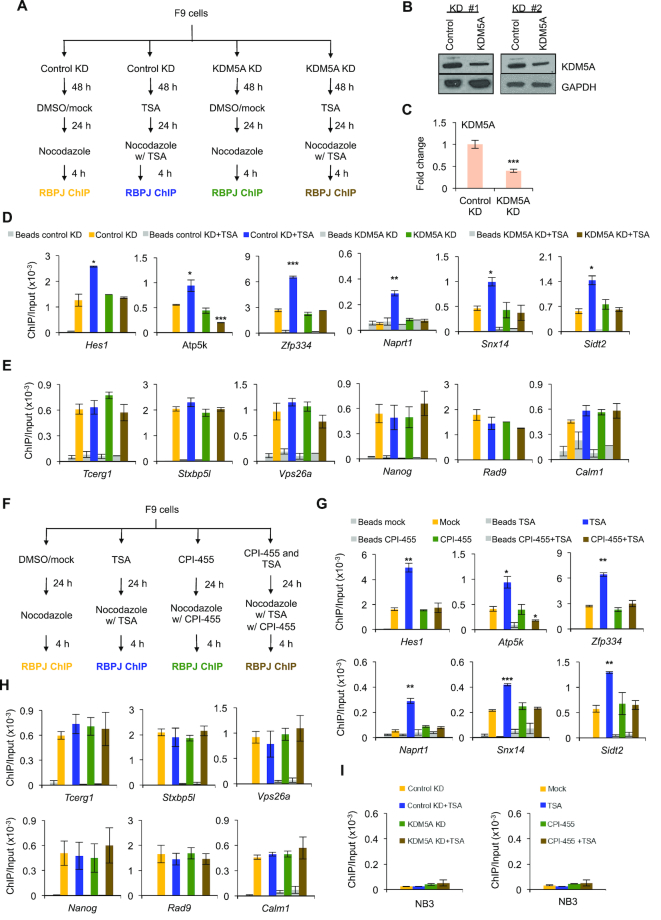
Figure 4.
The KDM5A knockdown or CPI-455 treatment reverses the effect of TSA on mitotic chromatin RBPJ occupancy. (A) Experimental scheme for D–E. F9 cells were subjected to TSA treatment, shRNA-mediated KDM5A knockdown, or a combination of these treatments. Mitotic cells were collected under the indicated experimental conditions and subjected to RBPJ ChIP-qPCR analysis. (B) Immunoblots showing the extent of KDM5A knockdown from two independent experiments. (C) Quantification of the data in b. (D) Enrichment of RBPJ at loci that contain the RBPJ-binding motif. (E) Enrichment of RBPJ at loci that do not contain the RBPJ-binding motif (F) Experimental scheme for G–H. F9 cells were subjected to TSA treatment, treatment with the inhibitor of H3K4 demethylation CPI-455, or a combination of these drugs. (G) Enrichment of RBPJ at loci that contain the RBPJ-binding motif. (H) Enrichment of RBPJ at loci that do not contain the RBPJ-binding motif. (I) Control ChIP assays analysing RBPJ enrichment at an RBPJ nonbinding region (NB3). Shown are means ± SEM from two biological replicates. Paired t-tests were performed to compare enrichment relative to untreated cells. *P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.001.