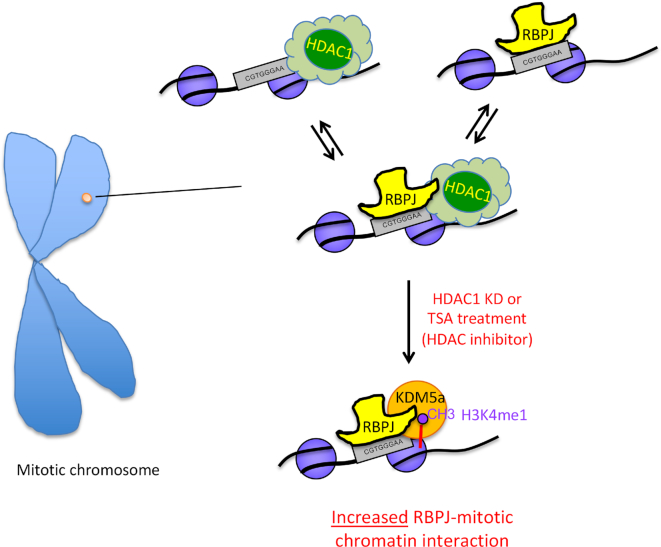
Figure 9.
Model depicting a regulatory mechanism for selective RBPJ binding on mitotic chromatin. RBPJ interacts dynamically with chromatin. The RBPJ-binding site can exist in at least three states: (i) with RBPJ bound, (ii) with RBPJ and an HDAC1-containing complex bound and (iii) with only an HDAC1-containing complex bound. Changes in transcription programs resulting from cell-signaling events could lead to changes in HDAC1 levels, activity or induce HDAC1 redistribution. This may lead to enhanced RBPJ–KDM5A interactions. Once KDM5A binds to RBPJ, it can catalyse the demethylation of trimethylated histone H3K4 to the di- and mono-methylated forms. Histone H3K4me1/me2 may further stabilize the chromatin association of KDM5A, and this may lead to lower rates of RBPJ dissociation from mitotic chromatin at sites containing the RBPJ-binding consensus sequence. Alteration in the affinity of RBPJ-containing complexes for mitotic chromatin through binding partner exchange may, therefore, be a mechanism to reinforce specific transcription programs through cell division.