Figure 3.
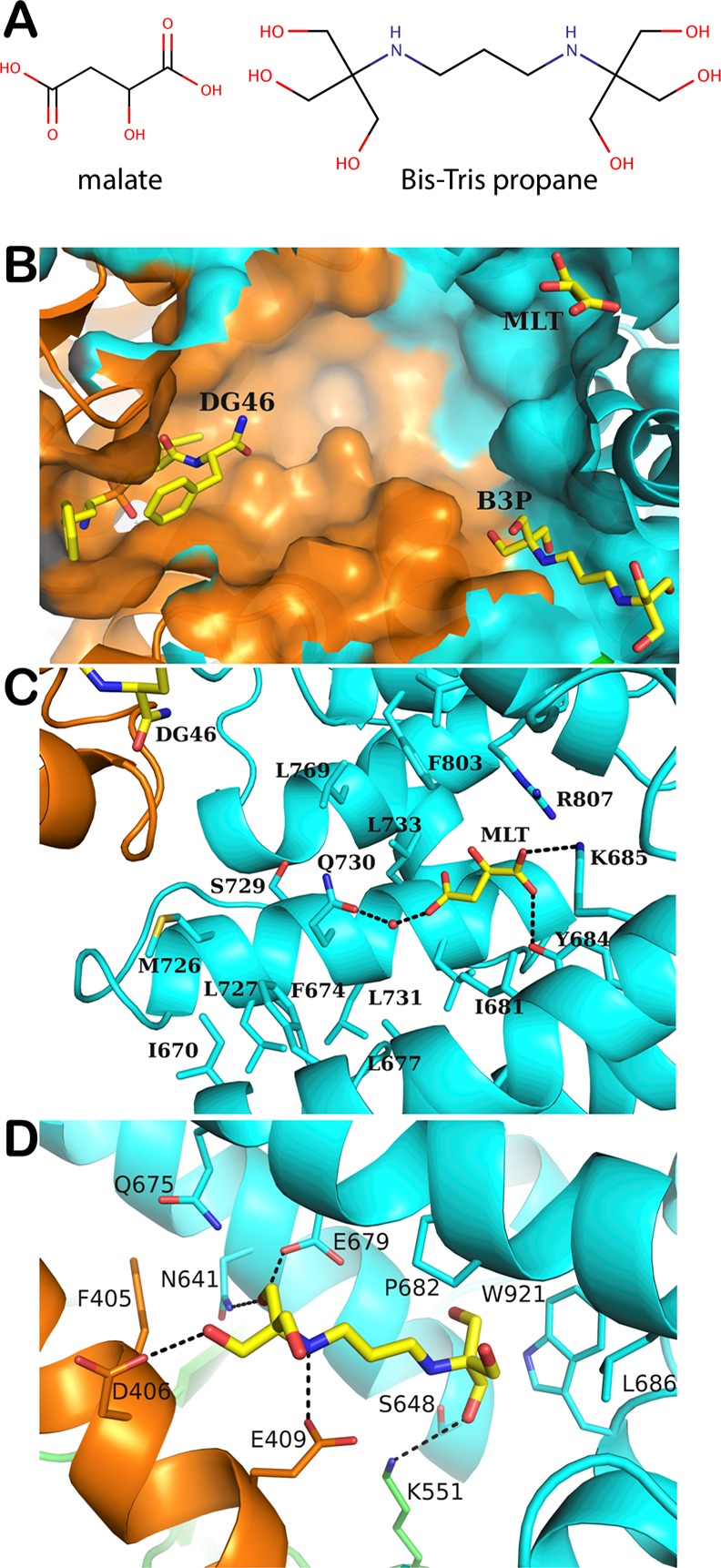
(A) Chemical structures of malic acid and bis-tris propane. (B) Bird’s eye view of the internal cavity of ERAP1 showing the binding of the inhibitor DG046, malic acid (MLT), and bis-tris propane (B3P) molecules. (C) Interactions between MLT and ERAP1 residues. (D) Interactions between B3P and ERAP1 residues. Domain II of ERAP1 is in orange and domain IV is in cyan. Carbon atoms are shown in yellow, oxygen atoms are in red, nitrogen in blue, phosphorus in orange.
