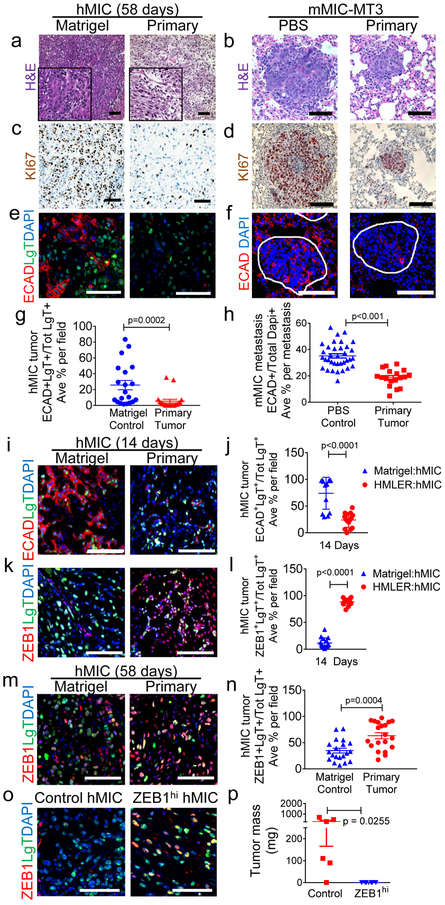
Figure 2. Primary tumors prevent differentiation and proliferation of distant MICs.
a-f, hMIC secondary tumors and mMIC-MT3 pulmonary metastases (per schematics in Fig. 1a, h) stained with: hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) (a, b); Ki67 (brown) and hematoxylin (nuclei; blue) (c, d); Immunofluorescence for E-cadherin (ECAD, red), Large T antigen to identify hMICs (LgT, green), and DAPI (nuclei, blue); lung metastases are circled in white (e, f). g-h, ECAD+ cells as % total number of LgT+ tumor cells (g) or DAPI+ cells (h) per microscopic field (ECAD in hMIC tumors n=20 images, representing 5 tumors/cohort; ECAD in mMIC-MT3 metastasis n=52 images, representing at least 18 metastases/cohort). i, j, Immunofluorescent images of hMIC tumors stained with ECAD (i) and quantified in (j). Matrigel cohort: n=15 images, HMLER cohort: n=13 images. k, l Immunofluorescent images of hMIC tumors stained with ZEB1 (k) and quantified in (l). Matrigel cohort: n=13 images, HMLER cohort: n=16 images. (j,l) presented as % Total number of LgT+ hMIC tumor cells. m, n, hMIC tumors (per Fig. 1a). Immunofluorescent images (m) and quantification (n) of ZEB1 staining (red) in hMIC tumors (positive for LgT antigen, green), as a percentage of total LgT+ cells. DAPI (nuclei, blue). Control n=20 independent images representing 3 tumors; HMLER cohort n=20 independent images representing 3 tumors. o, ZEB1 (red) and LgT+ tumor cells (green) in hMIC tumors from tumors in (p). DAPI (nuclei, blue). p, Final mass of hMIC tumors expressing either doxycycline-inducible control (Control hMIC; n=6 tumors) or ZEB1 cDNA (ZEB1hi hMIC; n=6 tumors). Scale bars=100 μm. Source data for g, h, j, l, n, p provided in Supplementary Table 1. 2-sided Mann-Whitney test (g, l); Welch’s 2-sided t test (h, n); 1-sided Welch’s t test (j,p).