Figure 4.
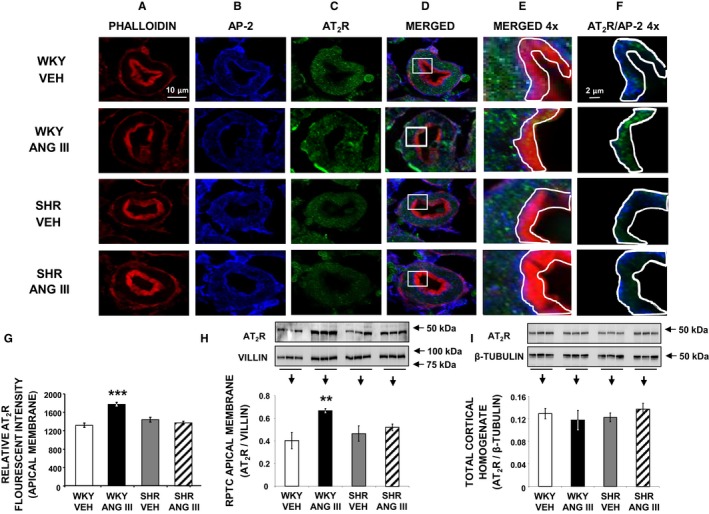
Confocal micrographs (×600 magnifications) showing AT 2R localization in female Wistar Kyoto (WKY) and spontaneously hypertensive (SHR) renal proximal tubule cell (RPTC) thin sections (5–8 μm) after renal interstitial (RI) infusion of vehicle (VEH) or angiotensin III (Ang III; 7.0 nmol/kg per min). As indicated, rows of images show a representative set of RPTCs from (top‐to‐bottom) WKY VEH, WKY Ang III, SHR VEH, and SHR Ang III treatment groups. As indicated, columns (left‐to‐right) depict brush border membrane staining with phalloidin (A), subapical area staining with adaptor protein‐2 (AP‐2) (B), AT 2R staining (C), merged image (D), enlarged merged image (×4) of the square section in (D) (E), and enlarged image with only AT 2R and AP‐2 staining of the brush border membrane area quantified for AT 2R (F). The encircled areas in (E and F) encompass brush border apical membranes quantified for AT 2R intensity. Scale bars in the first and sixth columns represent 10 and 2 μm, respectively. G, Quantification of RPTC apical membrane AT 2R fluorescence intensity performed on 20 independent measurements of RPTCs from 1 rat for WKY VEH (white bar), WKY Ang III (black bar), SHR VEH (gray bar), and SHR Ang III (striped bar) treatments. H and I, Depict Western blot analysis of AT 2R in RPTC apical membranes and total cortical homogenate, respectively, in WKY and SHR after VEH or Ang III (3.5–28.0 nmol/kg per min) infusions (N=6 for each condition). RPTC apical membrane signals were normalized to villin, a brush border apical membrane marker. Total cortical homogenates were normalized to β‐tubulin. Data represent mean±1 SE. **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001 compared with WKY VEH.
