Figure 3.
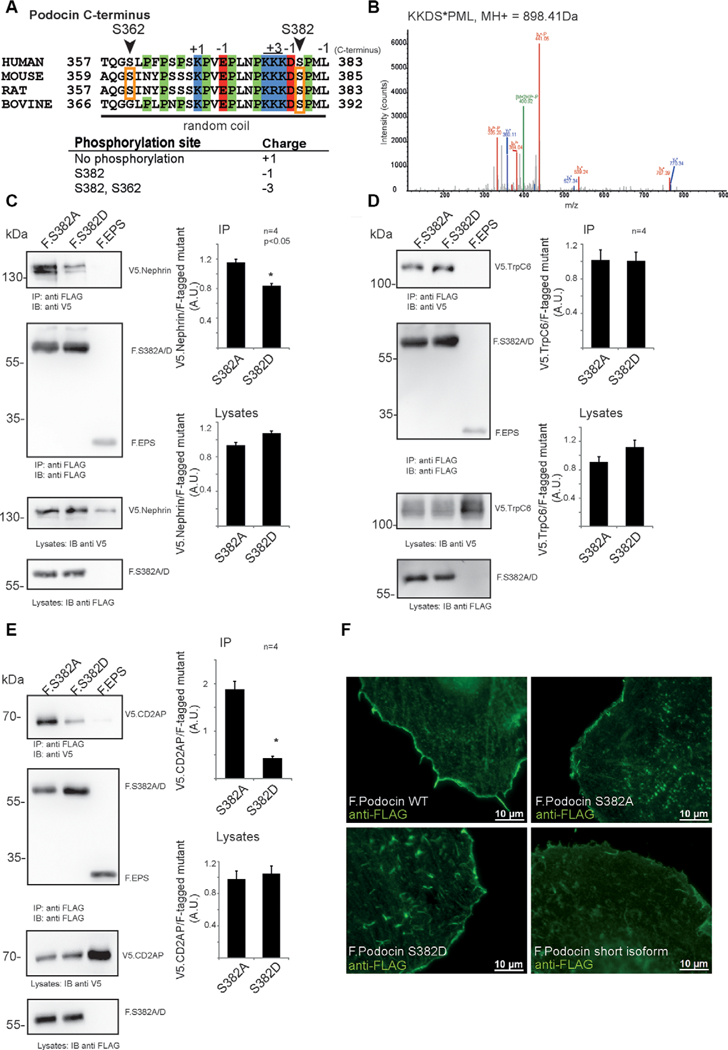
Characterization of Podocin S382 (murine sequence), a phosphorylation site discovered in mouse, rat, and bovine glomeruli. (A) Sequence of the C-terminal part of podocin, indicating a proline-rich random coil at the distal C-terminus. Phosphorylated residues are denoted by orange boxes. Site residue numbering is based on mouse sequence. (B) Evidence for phosphorylation of mouse podocin residue S382 in the protein expressed in HEK293T cells. (C)-(E) Coimmunoprecipitation of members of the slit diaphragm complex with FLAG-tagged phosphoablating (F.S382A) or phosphomimicking (F.S382D) mouse podocin expressed in 293Tcells. Protein complexes were purified using anti-FLAG antibody coupled to sepharose beads. All experiments were carried out in biologically independent quadruplicates. Bands were quantified using densitometry. p < 0.05 in a two-tailed, paired student’s t-test was considered significant. (C) Immunoprecipitation of sV5-tagged nephrin with FLAG-tagged phosphoablating or phosphomimicking mouse podocin mutants. (D) Immunoprecipitation of V5-tagged TrpC6 with FLAG-tagged phosphoablating or phosphomimicking podocin mutants. (E) Immunoprecipitation of sV5-tagged CD2AP with FLAG-tagged phosphoablating or phosphomimicking podocin mutants. (F) Localization of podocin wildtype and phosphoablating (F Podocin S382A) or phosphomimicking (F. Podocin S382D) mutant transiently expressed in HeLa cells. The podocin short isoform was used as a control protein which is not targeted to the membrane. Cells were stained using an anti-FLAG antibody. Appropriate negative controls were performed.
