Figure 2. Identification of glutathionylated proteins in HL-1 cells.
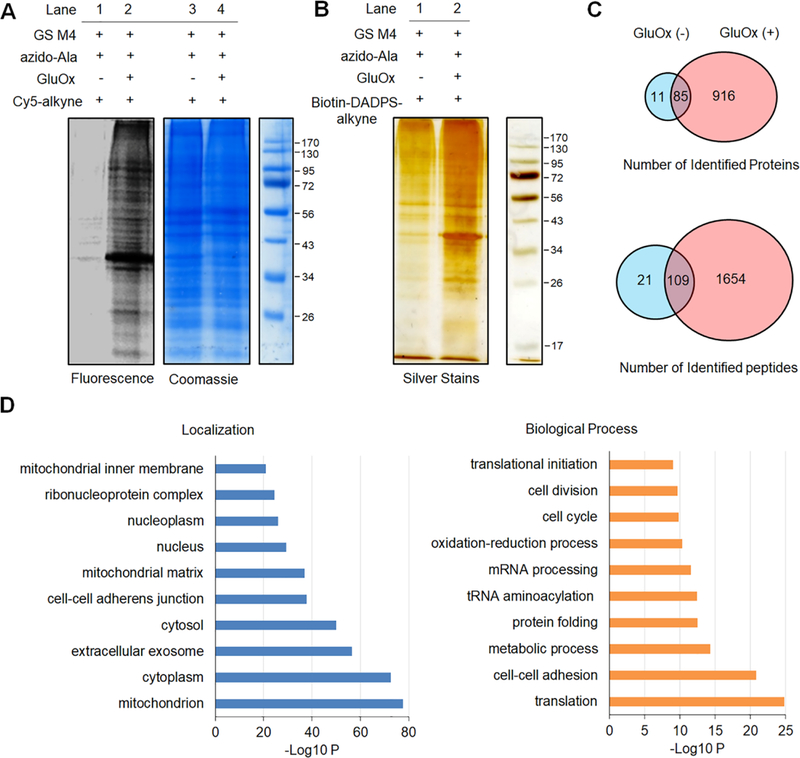
HL-1 cells expressing GS M4 were incubated with azido-Ala (0.6 mM) for 24 h and treated with glucose oxidase (GluOx, 6 units) for 10 min. (A) In-gel fluorescence detection of glutathionylated proteins. Collected lysates were subjected to click reaction with Cy5-alkyne for fluorescence detection. (B) Enrichment and elution of glutathionylated proteins. After click reaction of lysates with biotin-DADPS-alkyne, biotinylated glutathionylated proteins were bound to streptavidin-agarose, washed, eluted in an acidic cleavage condition (10% formic acid), and analyzed by silver staining. (C) The number of glutathionylated proteins and peptides under indicated conditions by LC-MS. Biotinylated glutathionylated proteins bound on streptavidin-agarose were digested by trypsin/Lys-C, eluted in an acidic cleavage solution, and analyzed by LC-MS/MS. (D) DAVID gene ontology (GO) analysis of identified glutathionylated proteins.
