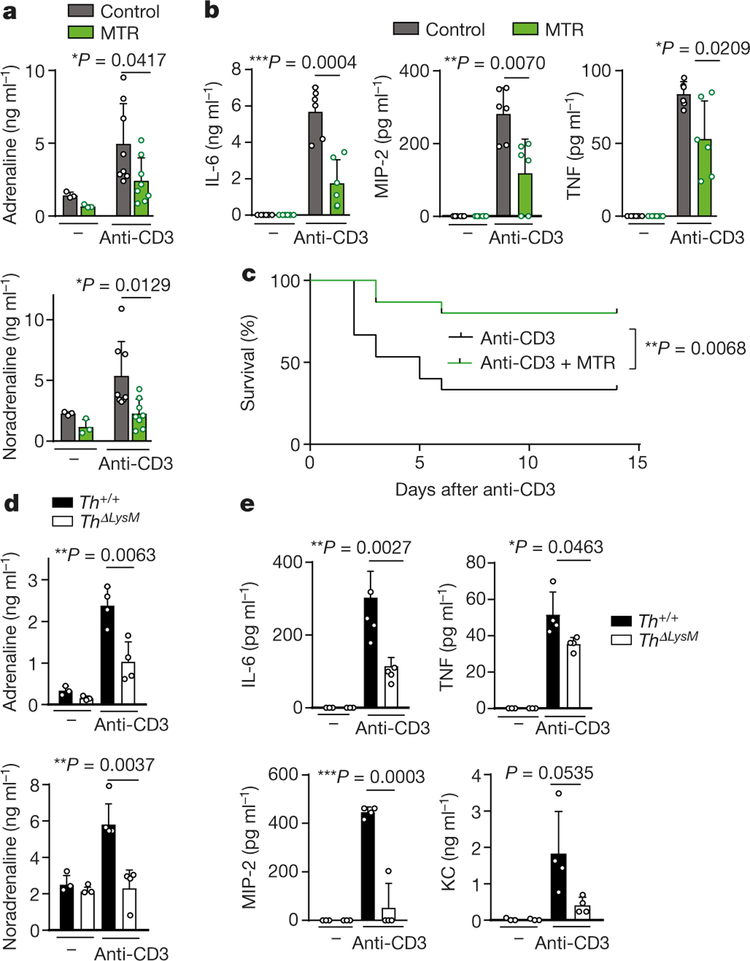
Fig. 3 |. Inhibition of catecholamine synthesis reduces CRS after anti-CD3 treatment.
a, b, Levels of adrenaline and noradrenaline (left to right, n = 3, 3, 8, 8 independent samples per column) (a) and of cytokines (n = 6 independent samples) (b) measured 24 h after anti-CD3 treatment, with or without MTR. c, Survival of BALB/c mice treated with anti-CD3, with or without MTR (n = 15 animals); analysed by two-sided log-rank test. d, e, Levels of adrenaline, noradrenaline (n = 3, 3, 4, 4) (d) and indicated cytokines (n = 3, 3, 4, 4) (e) measured 24 h after anti-CD3 treatment in Th+/+ or ThΔLysM mice. Data are presented as mean ± s.d. with individual data points shown, analysed by two-tailed t-test (a, b, d, e).