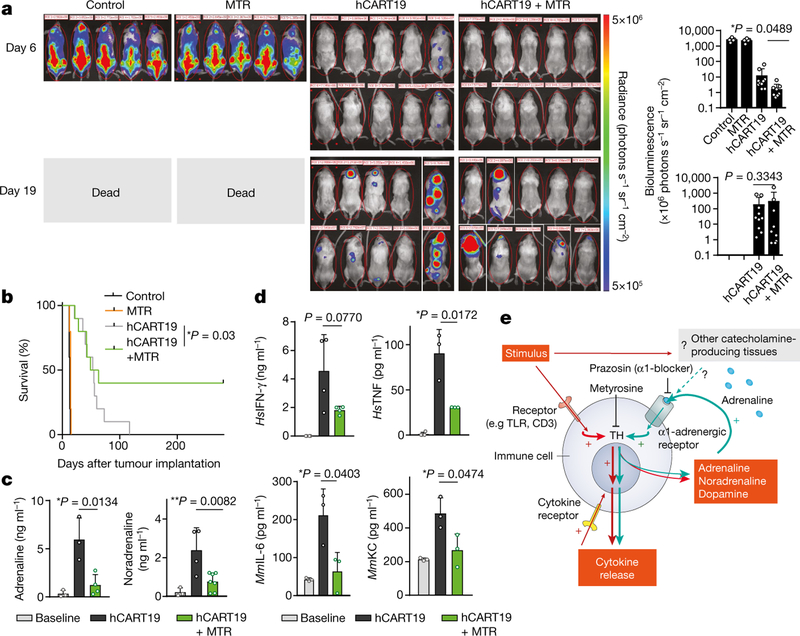
Fig. 5 |. Inhibition of catecholamine synthesis with MTR does not impair the therapeutic response of hCART19.
a, Serial bioluminescence imaging (BLI) of Raji-bearing NSGS mice (low tumour burden)at day 6 and 19 after treatment with 1.5 × 107 hCART19, with or without MTR (n = 10 mice per group) compared to control (UT-T), with or without MTR (n = 5 mice per group). BLI counts were used to quantify the tumour burden during the treatment course (right). Statistical differences were evaluated by one-tailed t-test. b, Corresponding Kaplan–Meier curve of Raji-bearing NSGS mice with low tumour burden, treated with 1.5 × 107 hCART19, with or without MTR pre-treatment (n = 10 mice per group) in comparison to control (UT-T), with or without MTR (n = 5 mice per group). Survival differences were analysed by weighted log-rank test (see Methods). c, d, Levels of plasma adrenaline (n = 3, 3, 4 per column) and noradrenaline (n = 3, 4, 7) (c) and HsIFN-γ (n = 4), HsTNF (n = 4, 3, 3), and mouse cytokines MmIL-6 (n = 3) and MmKC (n = 3) (d), assessed 72 h after hCART19 treatment. Data are presented as mean ± s.d. with individual data points shown, analysed by two-tailed t-test. e, Scheme showing how inhibition of the catecholamine pathway may reduce CRS. TLR, toll-like receptor.