Figure 1.
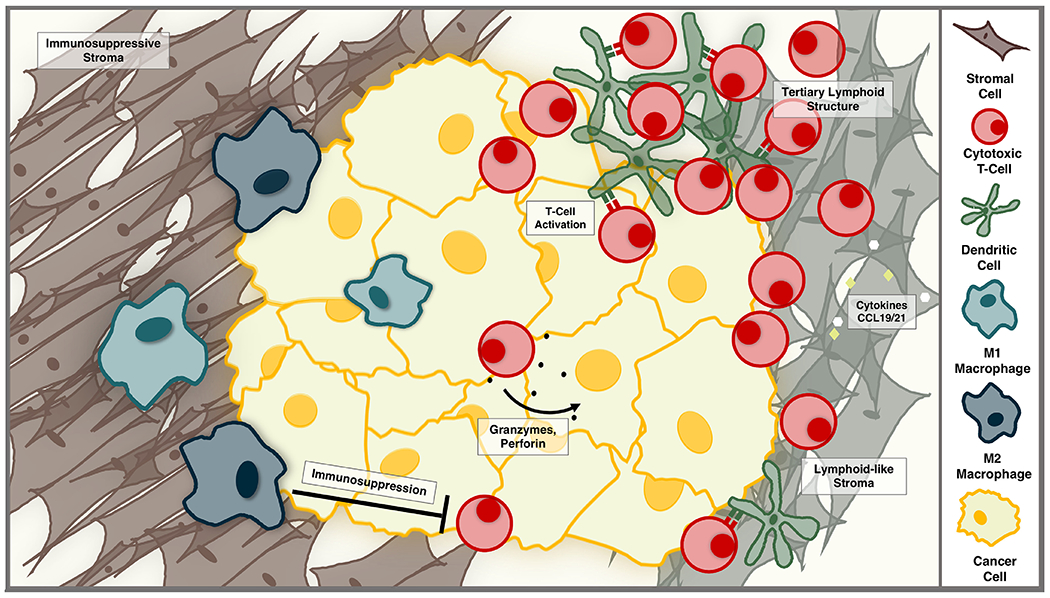
The tumor immune microenvironment can support or thwart the anti-tumor immune response. Infiltrating lymphocytes can kill tumor cells via cytotoxic granules containing granzymes and perforin. Dendritic cells and lymphocytes can organize, with the support of lymphoid-like stromal cells, to form tertiary lymphoid structures—dynamic aggregates that fuel the anti-tumor immune response. Alternatively, a dense, immunosuppressive stroma can limit T-cell activity, and pro-tumorigenic macrophages can support tumor growth and suppress cytotoxic T-cell activity.
