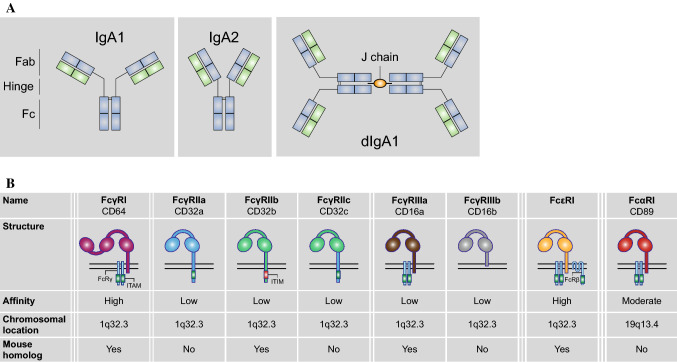
Fig. 1.
The human Fc receptor family. a IgA molecules consist of two domains, which are linked by a hinge region. IgA2 molecules have a shorter hinge region than IgA1, leading to a more Y-shaped conformation. The antigen-binding domain (Fab) binds to antigens, while the crystallizable fragment (Fc) domain can be recognized by Fc receptors. Furthermore, one molecule is made up of two identical heavy chains (in blue) and two identical light chains (in green). IgA molecules can be expressed as dimers when the Fc domains are connected to each other by a joining (J) chain. b Human FcRs are divided according to their binding capability to antibody subtype, FcγR, FcεR, and FcαR. FcγRs can be further subdivided into three types: FcγRI, FcγRII, and FcγRIII, which can be grouped based on their binding affinity to IgG (with FcγRI being the only high-affinity receptor). FcαRI is genetically located on a distinct location apart from the other receptors. The human FcR family differs quite significantly from the mouse FcR family