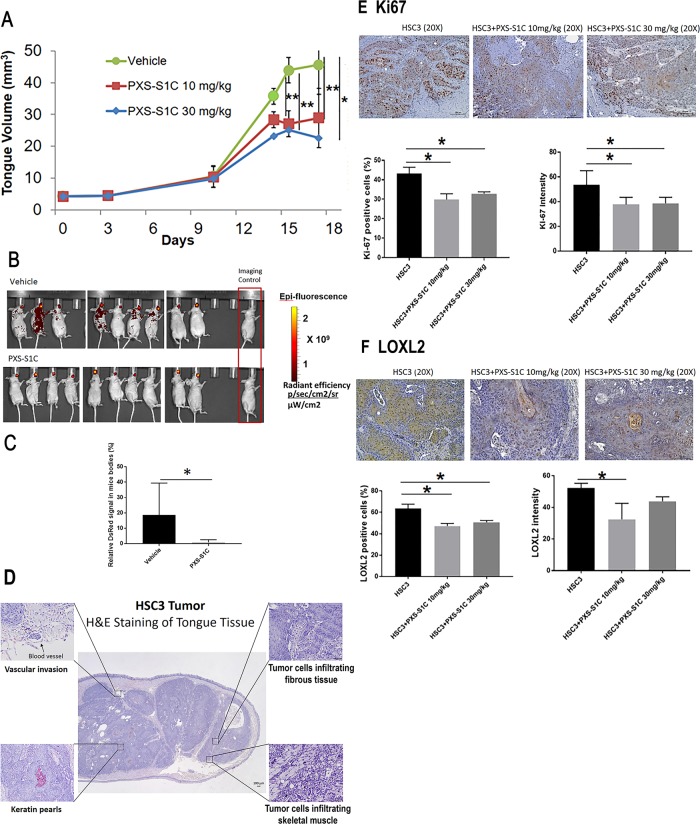
Fig. 2. LOXL2 promotes human tongue orthotopic cancer growth and metastasis in mice.
a PXS-S1C attenuates human tongue tumor growth in mice, and b and c PSX-S1C significantly decreases tumor cell spreading. Tumor volume of mouse tongues were measured every 3 days. Data are means ± SD. ANOVA, p: 0.0001, Tukey’s multiple comparisons test, **p < 0.001, ***p < 0.0001 indicate difference among the groups (n = 8 per group). b IVIS imaging for red fluorescent protein-labeled HSC3 cells 21 days after commencing injections of vehicle or PXS-S1C (30 mg/kg). The fluorescence signals were optimized for DsRed protein at excitation 570 nm and emission 620 nm. c Quantification of fluorescence signal area shows a significant difference between PXS-S1C-treated and non-treated groups. Data are mean ± SD. Student’s t-test, *p < 0.05 indicates difference between the groups. d Histology of HSC3 cell orthotopic tongue tumors. Hematoxylin and eosin staining a mouse tongue is shown 18 days after implantation. The photo is representative of histological features of HSC3 orthotopic tumors. The images were taken at ×4 and ×20 magnifications. Scale bar = 100 µm. PXS-S1C attenuates expression of (e) Ki67 and (f) LOXL2 in LY2 orthotopic tumors in immunodeficient mice. e Immunohistochemistry staining of tongue sections with anti-Ki-67 antibody shows that PXS-S1C reduced Ki-67 staining in orthotopic HSC3 tumors in mice. Scale bar = 100 µm. Data are mean ± SD. ANOVA, p < 0.01, Tukey’s multiple comparisons test, *p < 0.05 indicate difference among the groups (n = 8 per group). f Staining of tongue tissues with anti-LOXL2 antibody shows that PXS-S1C reduced LOXL2 staining in orthotopic HSC3 tumors in mice. Scale bar = 100 µm. Data are mean ± SD. ANOVA, p < 0.01, Tukey’s multiple comparisons test, *p < 0.05 indicate difference among the groups (n = 8 per group)