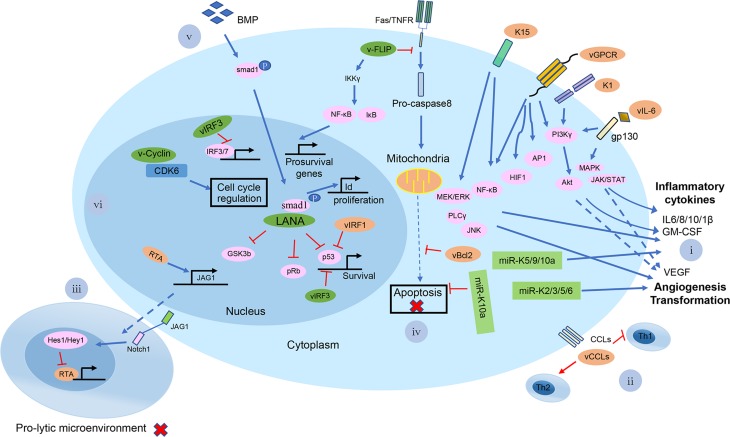
Fig. 7.
A brief summary of the possible mechanisms of KSHV-mediated pathogenesis at the cellular level. Shown in the diagram are viral lytic proteins in orange and viral latent proteins in green. (i) KSHV vGPCR, K1, K15, and vIL-6 proteins activate the PI3 Kγ/AKT, MAPK, JAK/STAT, NF-κB, MEK/ERK/JNK signaling pathways for infected cells to secrete a number of cytokines and chemokines, such as IL-6/8/10/1β, GM-CSF and VEGF; KSHV miR-K5/9/10a also induced the cytokines secretion. miR-K2/3/5/6 can induce angiogenesis-related factors, like VEGFA; (ii) KSHV encodes three chemokine homologs: viral CC-chemokine ligand-1-3 (vCCL1-K6, vCCL2-K4 and vCCL3-K4.1) to downregulate cellular immune response; (iii) KSHV RTA up-regulates the Notch ligand JAG1 by interacting with LEF1 and triggers Notch activation in neighboring cells. The activated Notch inhibits KSHV reactivation in those neighboring cells. It provides an insight into the mechanism by which a minority of viruses undergoes reactivation, while the majority maintains a persistent latent infection in KS tissues; (iv) v-FLIP in the infected cells inhibits the activation of pro-caspase-8 and has the ability to induce the expression of anti-apoptotic proteins via activation of NF-κB to upregulate pro-survival genes expression. vBcl-2, a homolog of cellular Bcl-2, inhibits apoptosis via tightly binding proapoptotic peptides. KSHV miR-K10a blocks TWEAK-induced apoptosis; (v) LANA affects the BMP signaling pathway and converts it to an oncogenic BMP-Smad1-Id pathway, which might contribute to the pathogenesis of KSHV-induced malignancies; (vi) KSHV LANA binds to and blocks p53-transcriptional activity to inhibit p53-induced cell death. LANA also binds and inactivates pRb, thereby removing the inhibition of pRb-induced cell cycle arrest. LANA binds to GSK-3β and thus accumulates unphosphorylated β-catenin, which in turn affects the cell cycle. v-Cyclin regulates the cell cycle and cell proliferation by constitutive activation of cellular cyclin-dependent kinase 6. vIRF-3 acts as a transcriptional activator on genes controlled by cellular IRF-3 and IRF-7. Further, vIRF-3 negatively regulates p53 protein stability, thereby inhibits p53-mediated activation of p21 gene transcription.