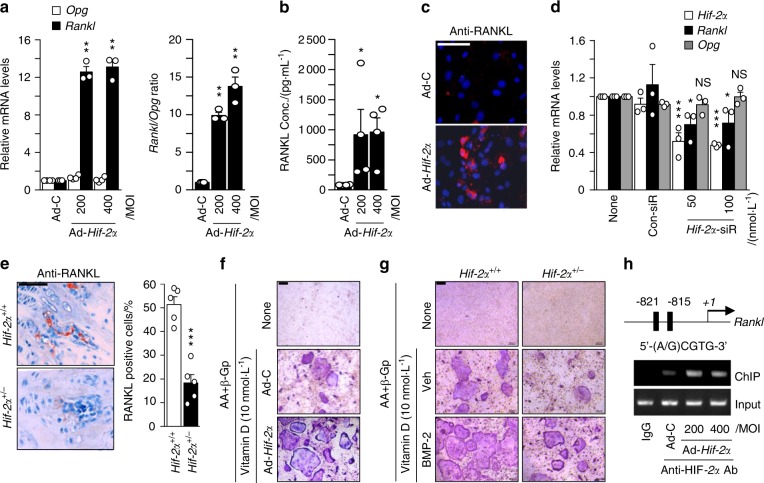
Fig. 3.
HIF-2α increases osteoblast-mediated osteoclastogenesis. a–c Primary calvarial preosteoblasts were infected with Ad-C or Ad-Hif-2α. qRT-PCR analysis of Rankl, Opg (left panel), and the Rankl/Opg ratio (right panel) (n = 3; a). ELISA analysis of secreted RANKL in culture media (n = 4; b) and detection of RANKL by immunofluorescence microscopy (scale bar: 100 μm; c). d Determination of Hif-2α, Rankl, and Opg expression following siRNA-mediated knockdown of HIF-2α in L-AA/β-GP-induced osteoblasts (n = 3). e RANKL immunostaining in bone obtained from Hif-2α+/+ and Hif-2α+/− mice. Scale bar: 100 μm. Rankl-positive osteoblasts were counted in the epiphyseal bone compartment. f Primary calvarial preosteoblasts infected with Ad-Hif-2α and BMMs were mixed and cocultured on glass covers, and TRAP staining was performed. g Osteoclasts derived from WT mice and osteoblasts from HIF-2α+/+ or HIF-2α+/− mice in the absence or presence of BMP-2 (100 ng/ml) were cocultured, and TRAP staining was performed (scale bar: 100 μm). h A ChIP assay of Ad-Hif-2α-infected osteoblasts was performed with anti-HIF-2α antibody and a primer pair designed to span the putative HIF-2α binding regions within the promoter of Rankl. Values are presented as the mean ± SEM (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.005; NS not significant)