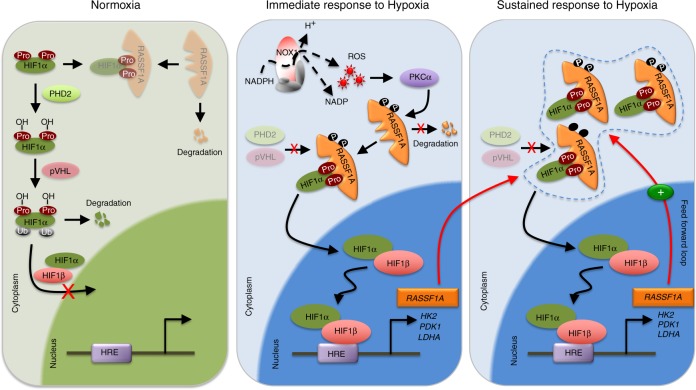
Fig. 9.
Schematic depicture of RASFF1A mediated HIF regulation. Under normoxia, HIF1α is hydroxlyated at proline residues by PHDs, ubiquitinated, followed by proteasomal degradation. Under hypoxia, RASSF1A is phosphorylated by ROS activated PKCα, leading to increased stability. Increased RASSF1A binds to HIF1α, preventing its binding to PHD2 and prolyl hydroxylation, increased nuclear translocation and subsequent transcriptional activity. This in turn leads to increased expression of glycolytic genes (PDK1, HK2, LDHA) and RASSF1A itself, giving rise to a feed forward loop and increased proliferation and glycolysis, manifesting in pulmonary hypertension and lung cancer pathogenesis. RASSF1A: Ras association domain family 1A, pVHL: von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein, PHD2/3: prolyl hydroxylase 2/3, HIF1α: hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha, HIF1β: hypoxia-inducible factor 1 beta, HRE: hypoxia-response elements, Ub: ubiquitin, OH: hydroxylation, Pro: proline, NADPH: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate hydrogen, ROS: reactive oxygen species, NOX1: NADPH oxidase 1, NADP: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, PKCα: protein kinase C alpha, P: phosphorylation, HK2: hexokinase 2, PDK1: pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase, isozyme 1, LDHA: lactate dehydrogenase A