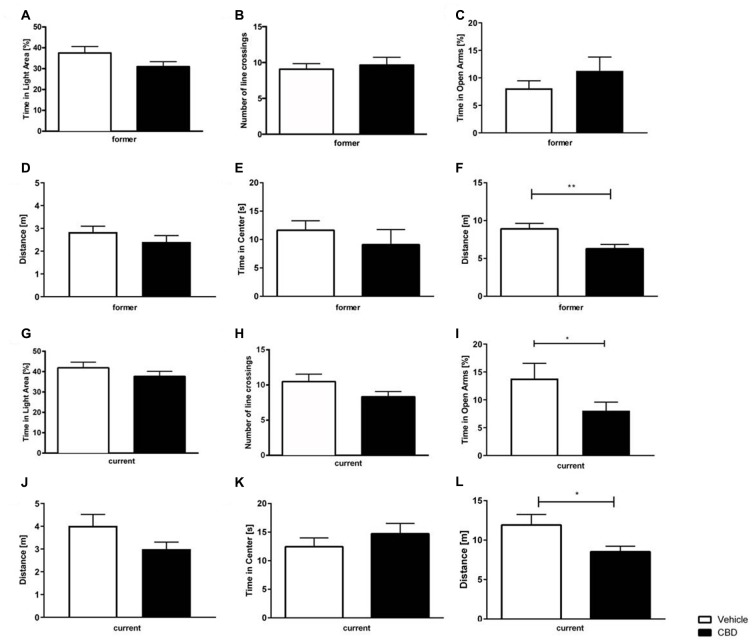
Figure 4.
Effects of prolonged CBD treatment on anxiety-related behavior. No significant difference in time spent in the light area in former CBD-treated mice (A). Number of line crossings as a confounding factor of mobility in the dark light box (DLB) did not significantly differ for the former treated group (B). Time spent in the open arms expressed as a percentage of total time spent in the maze (C) and traveled distance in the elevated plus maze (EPM) for former treated mice (D). In the open field (OF), there was no significant difference in time spent in the center of the box in former treatment group (E). Thus, a higher locomotor activity for vehicle-treated mice was found in the former CBD-treated mice (F). The time spent in the light area in current CBD-treated mice did not differ (G), as well as the number of line crossings in the DLB (H). Current CBD-treated mice showed a significant decrease in time spent in the open arms (I) but no difference in the distance traveled in the EPM (J). No significant difference between current CBD-treated mice and their vehicle-treated littermates in the time in the center (K), thus current CBD-treated mice traveled less distance in the OF (L). Unpaired t-test; n = 14–19, **p < 0.01; *p < 0.05. Data presented as mean ± SEM.