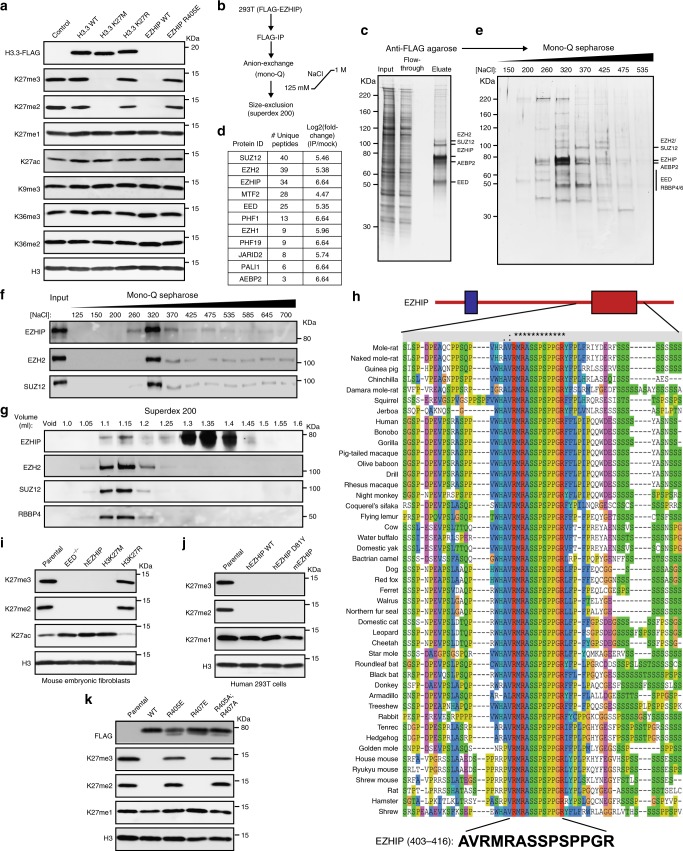
Fig. 1.
EZHIP forms a stable complex with PRC2 and lowers H3K27me3 in vivo. a Immunoblots of whole cell lysates generated from 293T cells expressing HA-FLAG-tagged H3.3 WT or K27M/R or FLAG-tagged EZHIP WT or R405E mutant. b Schematic showing the strategy for purification of EZHIP-associated proteins from 293T cells. c Silver stain of FLAG-tagged EZHIP association with PRC2. d Immunoprecipitated material from c were subjected to mass-spectrometry for protein identification and quantification. Proteins identified with at least 2 unique peptides and a log2 fold-change over the mock negative control of greater than 4 were considered hits. Protein abundances were calculated using ProteomeDiscoverer software. Complete list is provided as Supplementary Dataset 2. e Silver stained SDS-PAGE gel of mono-Q column fractions of M2 eluate from c. f, g Immunoblots displaying co-fractionation of EZHIP and PRC2 subunits on mono-Q and Superdex 200 columns, respectively. h Sequence alignment displaying the conserved 12 amino acid sequence in the EZHIP C-terminus. Red and blue domains represent the EZHIP conserved sequence and the site of hotspot mutations in PFA ependymomas respectively. i Immunoblots of lysates generated from mouse embryonic fibroblasts with EED knockout or expressing human EZHIP WT, H3K27M, or H3K27R. j Immunoblots of lysates generated from human 293T cell lines expressing human EZHIP WT or D81Y or mouse EZHIP. k Immunoblots of 293T expressing EZHIP WT, R405E, R407E or R405A;R407A mutants. Source images for Immunoblots are provided in a source data file