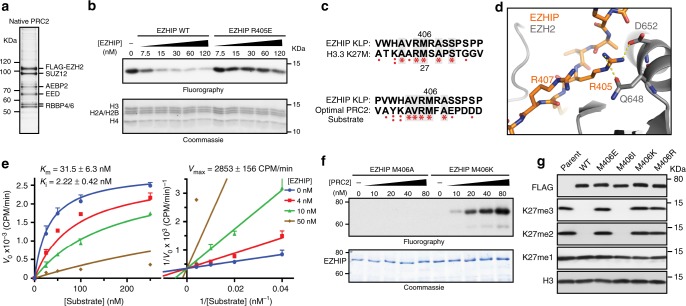
Fig. 2.
EZHIP is a competitive inhibitor of PRC2. a Silver stained SDS-PAGE gel showing the components of native PRC2 purified from HeLa cells. b In vitro methyltransferase reactions with PRC2 and oligonucleosome substrate. Full length recombinant EZHIP WT or R405E mutant purified from E. coli was titrated into the reaction mixture as shown. Half of the reaction was subjected to SDS-PAGE followed by fluorography and the other half was used for quantification by scintillation counting (Supplementary Fig. 2A). c Sequence alignment showing the similarity between lysine(27)-to-methionine mutated optimal PRC2 substrate and K27M-like EZHIP peptide (top), and H3K27M and K27M-like EZHIP peptide (bottom). d Formation of salt bridges between EZHIP R405 (or H3 R24) with EZH2 D652 (2.4 Å) and Q648 (3.5 Å), while R407 residue is exposed to solvent. e Increasing concentrations of oligonucleosome substrates were incubated with PRC2, SAM, and varying concentrations of EZHIP inhibitor. Ki was determined by fitting Michaelis-Menton and Lineweaver-Burk curves with competitive mode of inhibition. Error bars represent the standard deviation. ± represents standard error. f 0.3 µM EZHIP M406A or M406K mutant proteins were incubated with increasing concentrations of PRC2 with 1 µM 3H-SAM and 25 µM H3K27me3 peptide. Reactions were subjected to SDS-PAGE followed by fluorography. g Immunoblots of 293T expressing EZHIP WT or M406E/I/K/R mutants. Source data for Immunoblots and PRC2 assays are provided in source data file