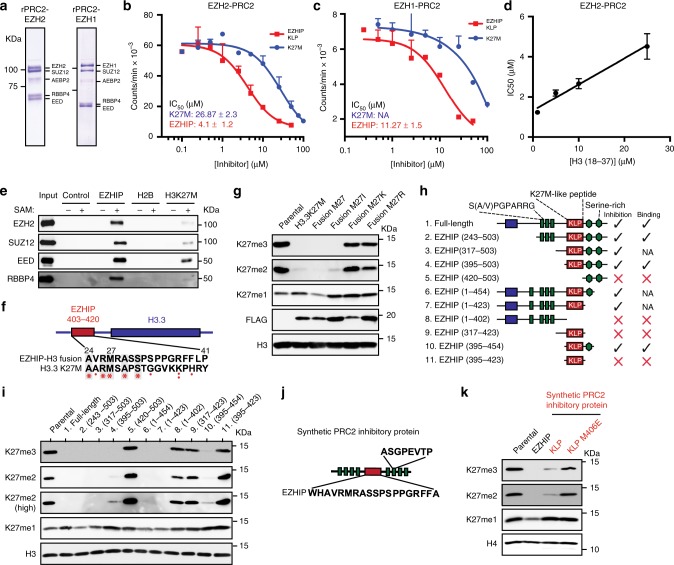
Fig. 3.
K27M-like Peptide sequence in EZHIP is necessary and sufficient to inhibit PRC2 activity. a Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE gel displaying the components of recombinant PRC2 purified from SF9 cells. b, c In vitro methyltransferase reactions with rPRC2-Ezh2 (b) or rPRC2-Ezh1 (c) and peptide substrates with increasing concentrations of EZHIP (403–423) or H3K27M (18–37) peptides. Variable slope, four parameter Hill curve was fitted to determine the IC50 of PRC2 inhibition under these conditions. ± represents standard error. d IC50 values of PRC2 inhibition by EZHIP peptide at different substrate (H3 (18–37)) concentrations (Supplementary Fig 3A) are plotted against the corresponding substrate concentrations. A linear positive correlation between IC50 and [substrate] is consistent with the competitive mode of inhibition. e Immunoblot of peptide pulldown of PRC2 and streptavidin agarose beads bound with biotinylated EZHIP (403–422), H2B (1–21) or H3K27M (18–37) peptides. f, g Immunoblots of whole cell extracts of 293T expressing HA-FLAG-tagged H3-EZHIP fusion protein (shown in f) with M27 or M27I/K/R mutants. h, i Immunoblots of 293T cells expressing truncated EZHIP protein as shown in h. Blue, red, and green boxes represent the hotspot for ependymoma-associated mutations, K27M-like peptide (KLP), and N-terminal short tandem repeats of EZHIP respectively, green hexagons represent serine-rich regions. j, k Immunoblots from lysates prepared from 293T cells expressing synthetic protein as shown in j. Green and red boxes represent short tandem repeats and KLP or K27M sequences respectively. Error bars represent the standard deviation. Source data for Immunoblots and PRC2 assays are provided in source data file