Figure 9.
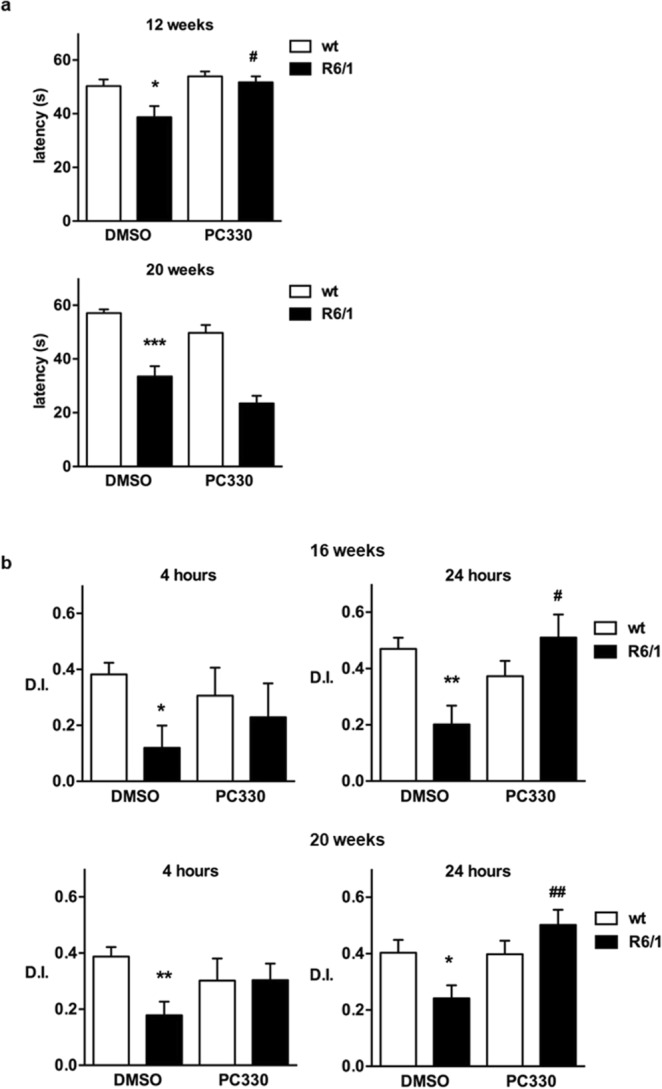
Behavioral assessment of IQM-PC330 effects in R6/1 mice. (a) Motor coordination was assessed using the rotarod test. The latency to fall was recorded in 12- and 20-weeks old wt or R6/1 mice. Mice of indicated genotypes received IQM-PC330 or vehicle (DMSO) in drinking water from shortly after weaning. The number of mice used (12 and 20 weeks, respectively): wt-DMSO (20–13), wt-PC330 (21–10), R6/1-DMSO (11–12), R6/1-PC330 (18–12). Data are shown as mean ± SEM. Nonparametric ANOVA, Kruskal-Wallis test (p values for both panels <0.0001) with Dunn’s multiple comparisons between selected groups was used. ***p < 0.005, *p < 0.05 vs wt-DMSO; #p < 0.05 R6/1-PC330 vs R6/1-DMSO. (b) The onset of cognitive impairment was assessed using the novel object recognition test in 16- and 20-weeks old wt or R6/1 mice that received the treatment in the drinking water as in (a). For a detailed protocol description see Supporting Information and the Material and Methods section in ref.11. The discrimination index (D.I.) reflects the ability to recognize novelty 4 or 24 h after first exposure to the object. The number of mice included in the novel object recognition test (16 and 20 weeks; 4 h and 24 h, respectively): wt-DMSO (27–32, 26–29), wt-PC330 (7–18, 7–16), R6/1-DMSO (21–37, 24–26), R6/1-PC330 (8–18, 9–15) Data are shown as mean ± SEM. Non-parametric ANOVA, Kruskal-Wallis test (p values; 16-weeks: 0.05 and 0.005 for 4 and 24 hours, respectively; 20-weeks: 0.003 and 0.009 for 4 and 24 hours, respectively; with Dunn’s multiple comparisons between selected groups was used, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05 vs wt-DMSO, ##p < 0.01, #p < 0.05 R6/1-PC330 vs R6/1-DMSO.
