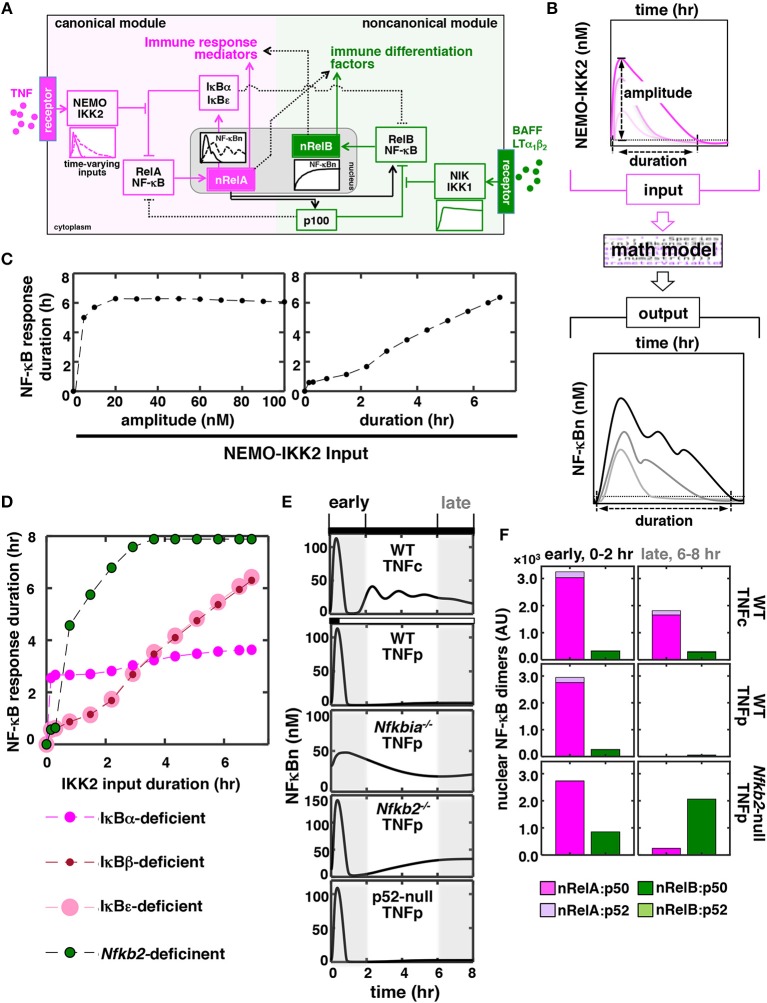
Figure 1.
In silico studies identify a role of p100 in discriminating between time-varying TNF inputs. (A) A graphical depiction of the NF-κB system. TNF through the canonical pathway (magenta) dynamically regulates the activity of RelA:p50 heterodimers, which mediate the expression of immune response genes. BAFF or LTα1β2 induces a distinct RelB NF-κB activity via a separate non-canonical pathway (green) for driving the expression of immune differentiation factors. However, these two NF-κB pathways are molecularly connected and display certain overlap in relation to gene expressions. Solid and dotted black lines represent major cross-regulatory mechanisms and those involving less-preferred biochemical reactions, respectively. NF-κBn, nuclear NF-κB activity. nRelA and nRelB represent corresponding nuclear heterodimers. (B) Schema describing in silico production function analyses. Briefly, theoretical IKK2 activity profiles of various peak amplitudes and durations were fed into the mathematical model, and NF-κBn responses were simulated in a time-course. Durations were estimated as the time elapsed above a specific threshold value, which was determined as the sum of the basal NF-κB or IKK activity and 5% of the corresponding basal-corrected peak activity, in the corresponding activity curves. (C,D) Graph plot of the duration of simulated NF-κBn responses as a function of the peak amplitude or the duration of theoretical IKK2 inputs. IKK2 activities of various peak amplitude but with invariant 8 h of duration (C, left) or with various durations but identical 60 nM peak amplitude (C, right and D) were used. Computational simulations involved (C) the WT system and (D) the indicated mutant systems. (E) In silico studies revealing NF-κBn responses in a time-course in WT and various mutant systems. Experimentally derived IKK2 activity profiles, obtained using MEFs treated with TNF either chronically (TNFc) or for 0.5 h (TNFp), were used as model inputs. Early (0–2 h) and late (6–8 h) phases have been marked using gray boxes. (F) Computational modeling predicting TNFp-induced nuclear activities of RelA and RelB heterodimers in WT and Nfkb2-null systems. Early and late activities were determined as the area under the corresponding activity curve between 0 and 2 h and 6–8 h, respectively, subsequent to correction for basal values. AU, arbitrary unit.