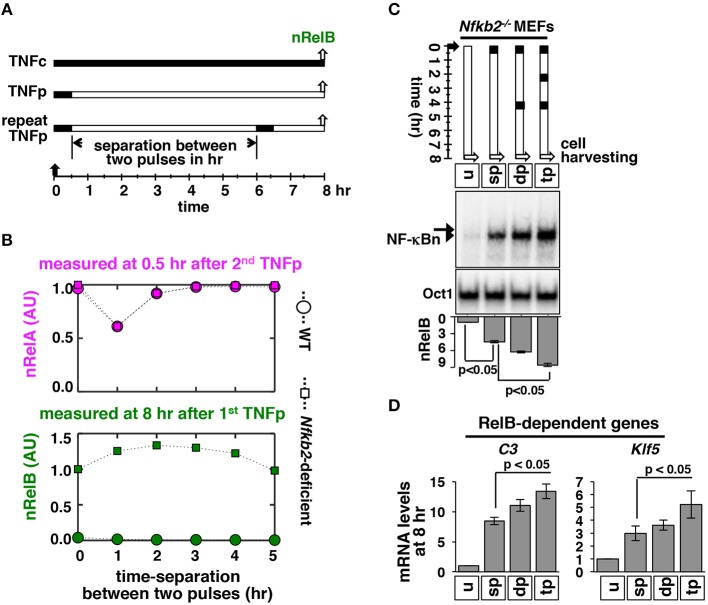
Figure 7.
Repeated TNF pulses of Nfkb2−/- cells strengthen late RelB:p50 signaling. (A) Schema describing repeated TNFp regime: the short-lived IKK2 input associated with the TNFp regime was fed into the model successively with varied separation time between two TNF pulses and corresponding NF-κBn was simulated. (B) Computational studies revealing the early nRelA activity induced 0.5 h after the second TNFp (top) and the late nRelB activity induced 8 h after the first TNFp (bottom) as a function of the separation time between two successive pulses in WT and Nfkb2-deficient systems. The early and late activities were normalized to those induced in response to a single pulse in the Nfkb2-deficient system. (C) Nfkb2−/− MEFs were treated with either a single TNFp (single pulse, sp) or two successive TNFp separated by 4 h (double pulse, dp) or three pulses at 2 h intervals (triple pulse, tp). Cells were harvested 8 h after the first pulse and analyzed for NF-κBn by EMSA. u denotes untreated. Bottom: quantitative analysis of the nRelB activities; data represent three experimental replicates. (D) Nfkb2−/− MEFs were subjected to the indicated treatments; cells were harvested 8 h after the first pulse and expressions of the indicated genes were measured by qRT-PCR. Bargraphs represent three biological replicates. Quantified data presented in this figure are means ± SEM of three biological replicates.