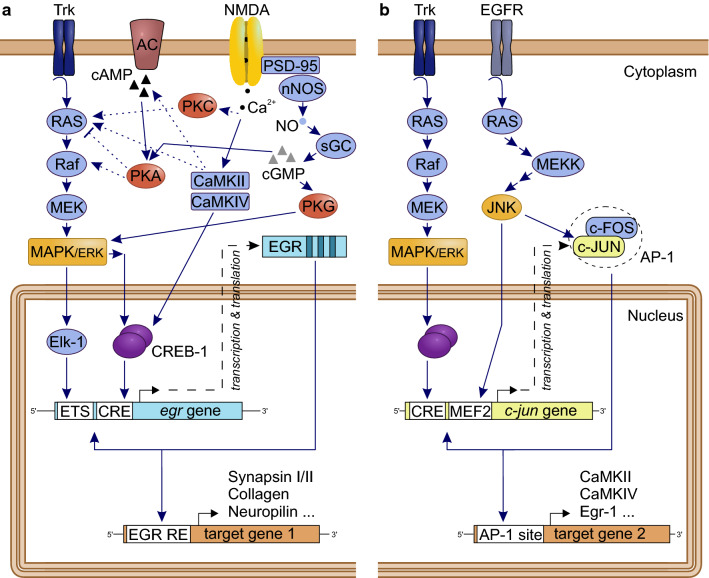
Fig. 3.
Potential cellular pathways and major players for the induction of the immediate early genes egr (a) and c-jun (b), and downstream targets, with focus on pathways previously linked to learning and memory in honey bees [42, 64, 85, 158]. a Activation of tyrosine receptor kinases (Trk) by neurotrophins induces via Ras (G protein) and Raf (kinase) the MAPK/ERK pathway, resulting in an activation of the transcription factors (TF) Elk-1 and/or CREB-1. By binding to their consensus target sequences (ETS and CRE sites), the TFs induce the transcription of egr. The Egr protein product in turn functions as a TF and activates the transcription of various late-response target genes. A list of candidate downstream genes in honey bees can be found in Khamis et al. [91]. Egr additionally auto-regulates its own expression by interacting with the promotor of the egr gene. Alternative regulation pathways include the cAMP-PKA signaling pathway and NMDA receptor-mediated activation of PKC or CaM kinases. b Activation of c-jun is also mediated by the MAP/ERK pathway. Another MAPK signaling pathway includes the c-jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK), which activates c-jun expression by binding of the MEF2 site in the promotor. c-Jun protein is regulated through phosphorylation by JNK and forms homo- or heterodimers (e.g., with c-Fos) resulting in the activator protein 1 (AP-1) complex, which regulates gene transcription via AP-1 binding sites on the DNA. c-Jun also auto-regulates its own transcription. Pathways compiled after [64, 112, 113, 135, 180–182]