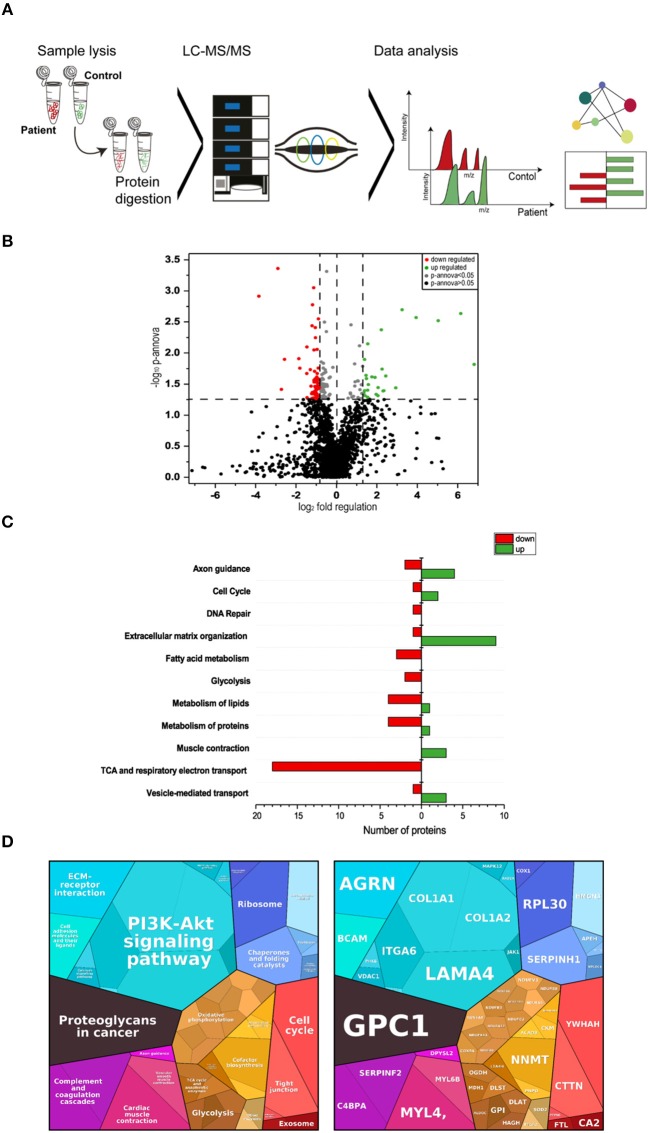
Figure 3.
Proteomic profiling of four MDC1A-patient derived muscles. (A) Methodological workflow applied in the study. (B) Results of our label-free proteomic profiling are shown as a volcano plot. All points (each one represents a protein) over the horizontal line have a statistically significant p-ANOVA of ≤0.05. In total, 51 proteins are decreased (red points) and 35 proteins are increased in abundance (green points) in laminin-211-deficient skeletal muscle. (C) Results of an in silico pathway analysis of proteins altered in abundance utilizing DAVID, KEGG, and Reactome platforms indicating alterations of ECM protein composition, cellular metabolism, axon guidance, cell cycle, and DNA repair, muscle contraction and of vesicular protein transport. (D) Results of an in silico pathway analysis of proteins altered in abundance utilizing Proteomap platform confirming the perturbed cellular functions indicated by the results of the previous pathway analysis and moreover indicating perturbed function of cellular signaling cascades such as PI3K-Akt signaling.