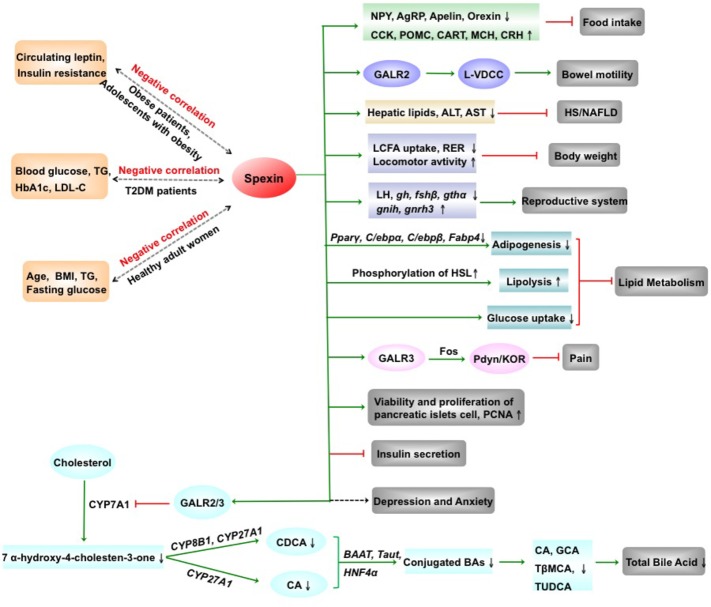
Figure 2.
The physiological and pathophysiological effects of spexin. AgRP, agouti gene-related protein; ALT, alanine transaminase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; BAAT, bile acid CoA: amino acid N-acyltransferase; BAs, bile acids; BMI, body mass index; CA, cholic acid; CART, cocaine-amphetamine regulated transcript; CCK, cholecystokinin; CDCA, chenodeoxycholate; CRH, corticotropin-releasing hormone; CYP27A1, sterol 27-hydroxylase; CYP7A1, cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase 1; CYP8B1, sterol 12α-hydroxylase; fshβ, follicle-stimulating hormone β; GalR2, galanin receptor 2; GalR3, galanin receptor 3; GCA, glycocholate; gh, growth hormone; gnih, gonadotropin inhibitory hormone; gnrh3, gonadotropin-releasing hormone 3; gthα, gonadotropin hormone α; HbA1c, hemoglobin A1c; HNF4α, hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha; HS/NAFLD, hepatic steatosis/nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; KOR, κ-opioid receptor; LCFA, long-chain fatty acid; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol; LH, luteinizing hormone; L-VDCC, L-type voltage-dependent calcium channel; MCH, melanin-concentrating hormone; NPY, neuropeptides Y; PCNA, proliferating cell nuclear antigen; Pdyn, prodynorphin; POMC, proopiomelanocortin; RER, respiratory exchange ratio; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus; Tβ-MCA, tauro-β-muricholate; taut, taurine transporter gene; TG, triglyceride; TUDCA, tauroursodeoxycholate; ↑, increase; ↓, decrease; green arrow, promotion; red arrow, inhibition. (Partial figure originated from Lin et al., 2018a,b).