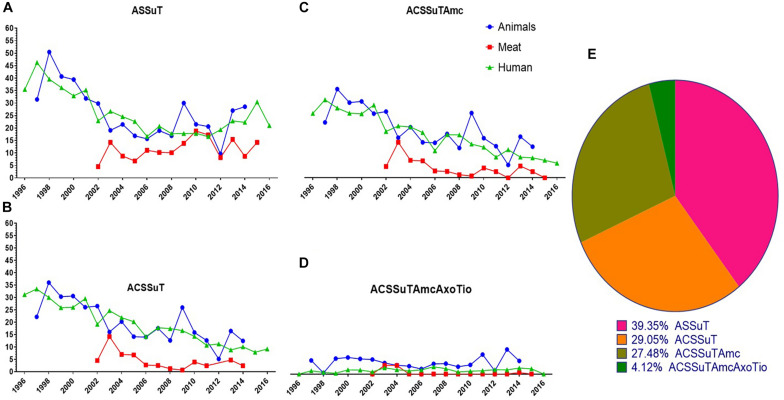
FIGURE 4.
Graphical representations of four antibiotic resistance patterns (ASSuT, ACSSuT, ACSSuTAmc and ACSSuTAmcAxoTio) found in S. Typhimurium strains through 1996–2016 in United States. (A) ASSuT (Ampicillin, Streptomycin, Sulfonamides, and Tetracycline) resistance patterns found in S. Typhimurium isolates from animals, meat and humans. Though the ASSuT resistance in animal and human isolates of Typhimurium declined sharply during 2002–2008, the resistance is on rise in the recent years. The ASSuT resistance in meat isolates showed increasing pattern with time. (B) ACSSuT (Ampicillin, Chloramphenicol, Streptomycin, Sulfonamides, and Tetracycline) resistance patterns found in S. Typhimurium isolates from animals, meat and humans. The ACSSuT resistance in human and meat isolates of Typhimurium showing decreasing pattern but the same resistance in animal isolates showing increasing trend with the time. (C) ACSSuTAmc (Ampicillin, Chloramphenicol, Streptomycin, Sulfonamides, Tetracycline, and Amoxicillin-clavulanic acid) resistance patterns found in S. Typhimurium isolates from animals, meat and humans. The ACSSuTAmc resistance in human and meat isolates of Typhimurium showing decreasing pattern but in animal isolates the resistance remained high with time. (D) ACSSuTAmcAxoTio (Ampicillin, Chloramphenicol, Streptomycin, Sulfonamides, Tetracycline, Amoxicillin-clavulanic acid, Ceftriaxone, and Ceftiofur) resistance patterns found in S. Typhimurium isolates from animals, meat and humans. ACSSuTAmcAxoTio resistance in animal isolates showed increasing tendency in the recent years. The XX’ presents the time of data collection while YY’ gives the percent of resistance. (E) Pie chart showing the percentage of distribution of four different resistance patterns among 7237 isolates of S. Typhimurium from animals, meat and humans.