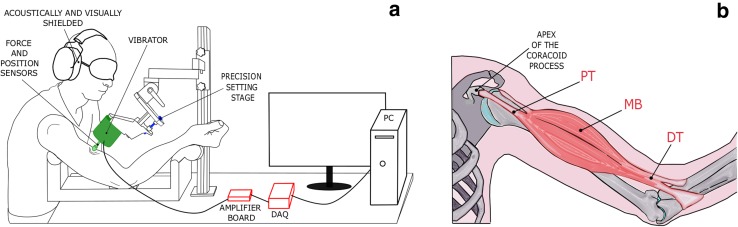
Fig. 1.
Experimental setup. a The setup comprised a PC, a data acquisition board (DAQ), a signal amplifier board and a vibrator. The vibrator was equipped with position and force sensors. The subjects were seated with the elbow angle at around 120°. They were wearing headphones (to avoid distraction due to the noise produced by the vibrator) and were blindfolded (to avoid incongruent visual feedback of the arm, which can disrupt the illusion (Guerraz et al. 2012)). The precision setting stage supporting the vibrator guaranteed a fine control of the applied preload force. b Location of the stimulated points (in red). DT indicates the distal tendon, MB the muscle belly and PT the proximal tendon. The apex of the coracoid process was used as an anatomical landmark to localize the PT