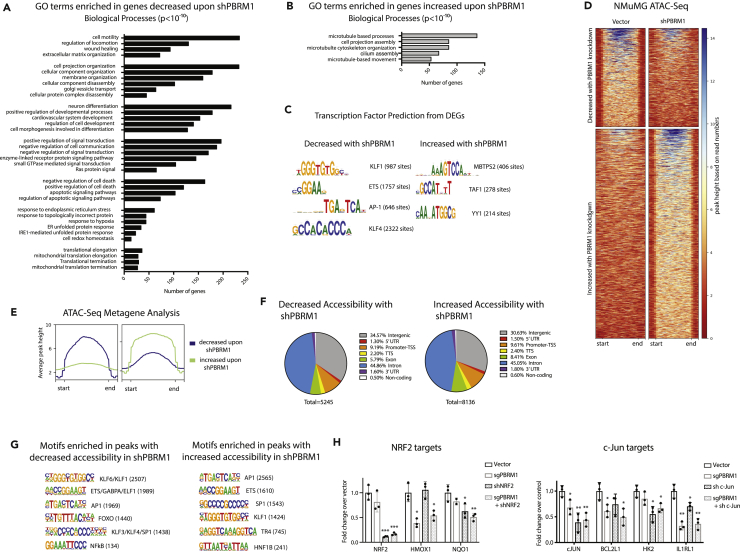
Figure 2.
PBRM1 Regulates Genes Involved in Cell Adhesion, Signaling, Stress Response, and Apoptosis and Is Predicted to Cooperate with Transcription Factors Involved in Response to Stress
(A) Top overrepresented biological process GO terms (p values < 10−10) for differentially expressed genes that are downregulated in NMuMG cells with shPBRM1.
(B) Top overrepresented biological process GO terms (p values < 10−10) for differentially expressed genes that are upregulated in NMuMG cells with shPBRM1.
(C) Putative transcription factors were identified for genes exhibiting differential expression in NMuMG cells with shPBRM1.
(D) Heatmaps of regions identified as differentially accessible with PBRM1 knockdown using ATAC-seq analysis of NMuMG cells. Regions of at least 1.5-fold differential accessibility were calculated between pooled samples of three biological replicates.
(E) Metagene plots of the regions identified as differentially accessible with PBRM1 knockdown using ATAC-seq analysis of NMuMG cells.
(F) Genomic elements associated with the differentially accessible peaks. The overall distribution was calculated as a percentage of the total differentially accessible regions for each condition.
(G) Motif analysis was performed using HOMER for the differentially accessible peaks. Statistically significant motifs were identified based on relative enrichment over genomic areas with similar AT content.
(H) The contribution of PBRM1 to the transcriptional regulation of NRF2 (left) or c-Jun (right) target genes using qRT-PCR and OAZ1 as the housekeeping gene. n = 3. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (paired Student's t test). Error bars represent SD.