Figure 1.
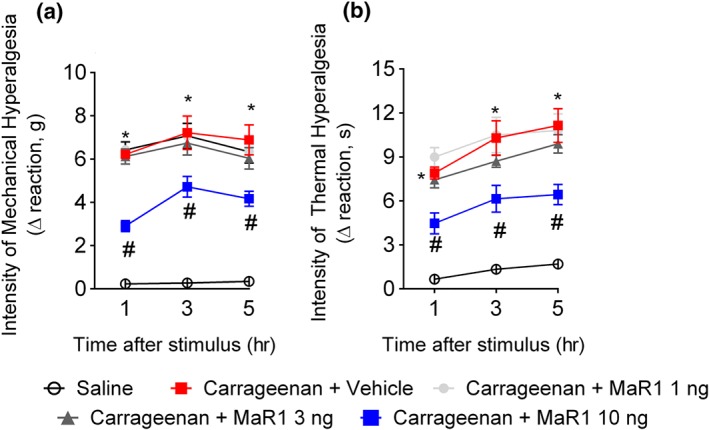
MaR1 reduces carrageenan‐induced mechanical and thermal hyperalgesia. Mechanical hyperalgesia (a) and thermal hyperalgesia (b) were evaluated 1, 3, and 5 hr after intraplantar injection of carrageenan (100 μg per paw). Results from mechanical hyperalgesia are presented as Δ withdrawal threshold (in g) and for thermal hyperalgesia as Δ withdrawal threshold (in s), which was calculated by subtracting the mean measurements at 1–5 hr after carrageenan from the zero‐time (baseline values) mean measurements. MaR1 reduced carrageenan‐induced mechanical (a) and thermal (b) hyperalgesia. Results are representative of two independent experiments and are presented as mean ± SEM of measurements, n = 6 mice per group per experiment (*P < 0.05 vs. saline, # P < 0.05 vs. 0 mg·kg−1 group; two‐way repeated measures ANOVA followed by Tukey's post‐test)
