Figure 6.
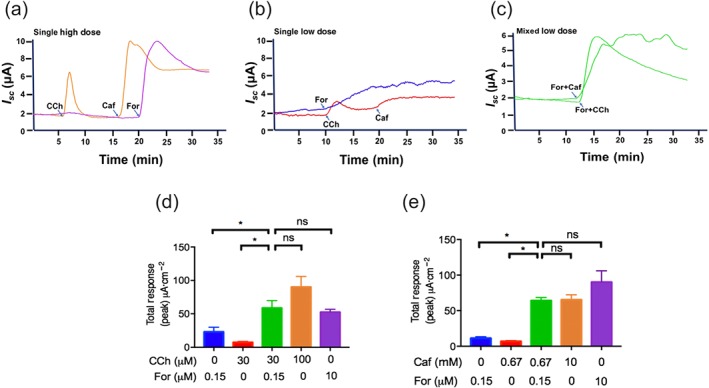
The synergistic effects of forskolin, caffeine, and carbachol in duodenal epithelial anion secretion. (a–b) Representative time courses of duodenal I sc after serosal addition of single high dose or single low dose of carbachol (CCh, 100 or 30 μM, n = 5), caffeine (Caf, 10 or 0.67 mM, n = 5), or forskolin (For, 10 or 0.15 μM, n = 5). (c) Representative time courses of enhanced duodenal I sc after serosal addition of mixed low doses of forskolin (For, 0.15 μM) plus caffeine (Caf, 0.67 mM), or forskolin (For 0.15 μM) plus carbachol (CCh 30 μM). Please note the synergistic effects of forskolin and caffeine (or CCh) after their combinations by comparing Figure b with Figure c. (d–e) Summary data obtained from Figure a–c showing the synergistic effects of forskolin and caffeine (or CCh) in duodenal epithelial anion secretion. * P < 0.05 significantly different from the corresponding control, ns: no significant differences
