Figure 10.
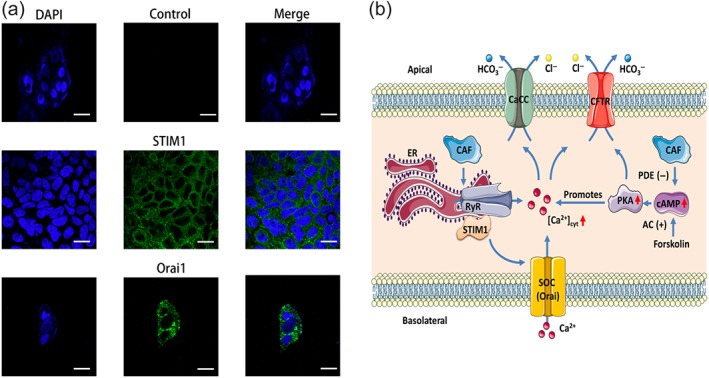
STIM1/Orai1 in human intestinal epithelial cells and schematic diagram depicting the proposed mechanisms of caffeine‐mediated intestinal anion secretion. (a) The left panels showing the nuclei of the Caco‐2 cells stained with DAPI (blue). The middle panel on the first row showing cell image without the primary antibodies against STIM1 and Orai1 as a negative control. The middle panels on the second and third rows showing the specific staining to STIM1 and Orai1 proteins in the cells. The right panels showing the merge of left and middle panels. Each one is the representative of three independent experiments with similar results. Scale bar = 20 μm for each image. (b) The proposed mechanisms. Caffeine (CAF) predominantly activates RyR in the ER to induce Ca2+ signalling probably through STIM/Orai channels and then to stimulate Ca2+‐mediated intestinal anion secretion through CaCC and CFTR channels. Caffeine‐evoked Ca2+ signalling also synergizes the effect of cAMP signalling through activation of PKA. Furthermore, caffeine slightly raises cAMP by inhibiting PDE. AC (+): activation of adenylyl cyclase; CaCC: Ca2+‐activated Cl− channels; Caf: caffeine; CFTR: cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator; PDE (−): inhibition of PDE; RyR: ryanodine receptor; SOC: store‐operated channels
