Fig. 1.
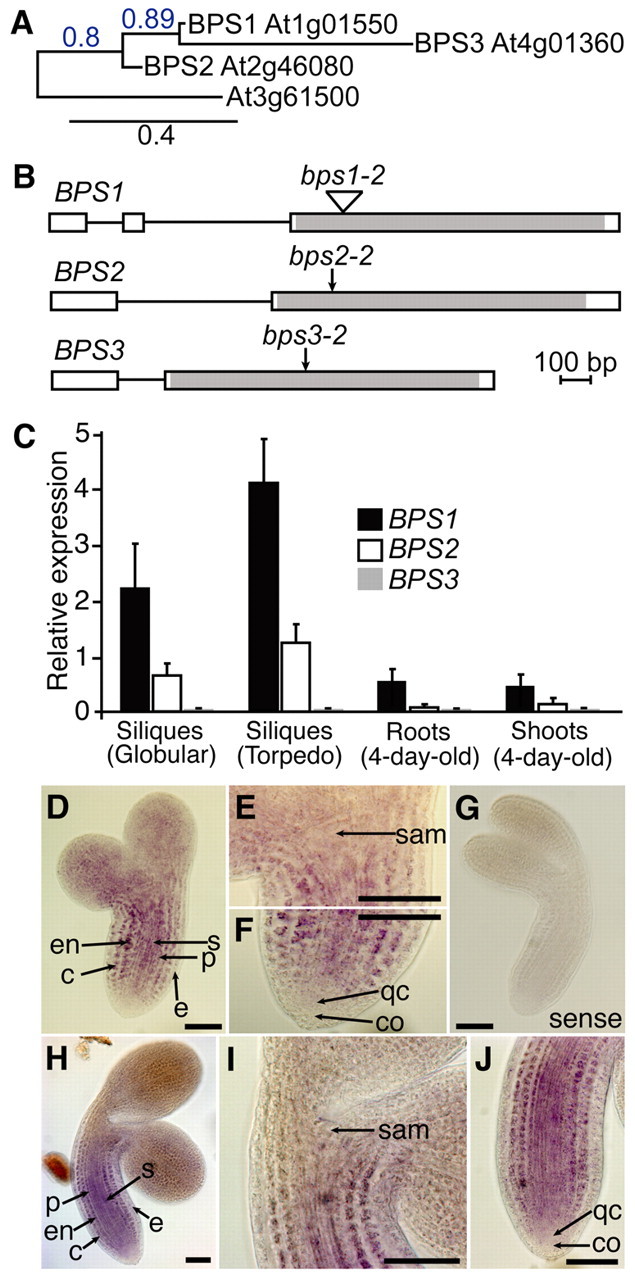
The Arabidopsis BYPASS gene family encodes conserved proteins that are predominantly expressed in siliques. (A) An unrooted phylogenetic tree based on amino acid sequences of Arabidopsis BPS gene family members reveals a close relationship between BPS1, BPS2 and BPS3. (B) The gene structure of BPS1, BPS2 and BPS3 reveals a very similar organization of exons (boxes) and introns (lines), with the coding region restricted to the 3′-most exon. Mutation sites for alleles used in this study are indicated by arrows. (C) Relative expression of BPS1, BPS2 and BPS3 in select tissues. Error bars are s.d. (D-J) In situ hybridization of BPS1 in wild-type embryos. (D-G) Torpedo-stage embryos; (D-F) hybridization with antisense probe and (G) Sense probe. The shoot apical meristem and root meristem regions are shown at higher magnification in E and F, respectively. (H-J) Bent-cotyledon stage embryos; (I) SAM and (J) RAM of embryo shown in H. Scale bars: 50 μm. c, cortex; co, columella; e, epidermis; en, endodermis; p, pericycle; qc, quiescent center; s, stele; sam, shoot apical meristem.
