Fig. 3.
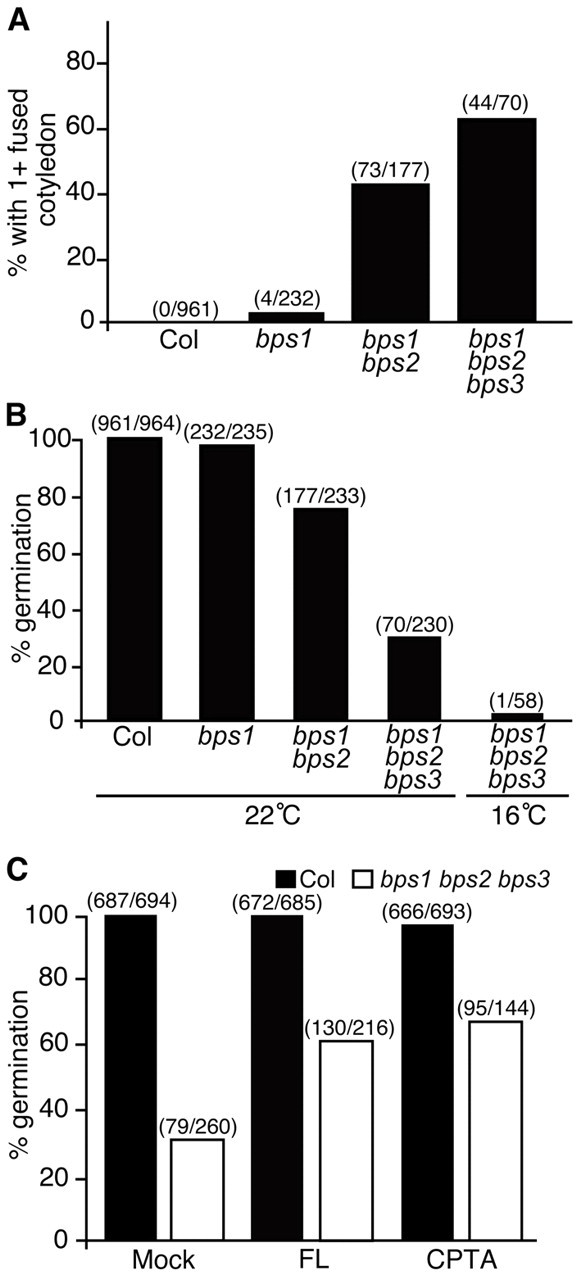
Germination and cotyledon formation are sensitive to loss of BPS activity. (A) Quantitative analysis of the cotyledon fusion phenotype revealed increased penetrance in higher-order mutants. (B,C) Quantitative analysis of germination rates in bps single and multiple mutants (B) and in wild type (Col-0) and bps triple mutants from siliques treated with the carotenoid biosynthesis inhibitors FL and CPTA (C). The partial suppression of germination defects in bps triple mutants indicated that this phenotype required carotenoid biosynthesis, and that the activity of all three BPS gene products prevent synthesis of the bps signal. These analyses are based on the number of homozygous mutants (see supplementary material Table S3). The number of observed mutants and the number of expected mutants are listed above each bar on all three graphs.
