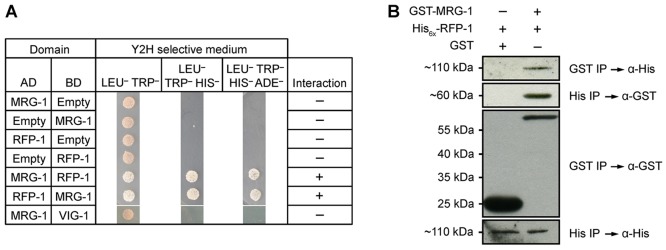
Fig. 4.
MRG-1 and RFP-1 physically interact. (A) Yeast two-hybrid screen showing interaction between MRG-1 and RFP-1. Yeast strains contain activation domain (AD) and DNA-binding domain (BD) vectors with no insert (Empty), full-length mrg-1 cDNA or full-length rfp-1 cDNA. Growth on Leu–Trp– medium indicates successful co-transformation, growth on Leu–Trp–His– indicates interaction, and growth on Leu–Trp–His–Ade– indicates strong interaction. vig-1 was used as an unrelated negative control. (B) Bacterial co-immunoprecipitation followed by western blot confirms the interaction between MRG-1 and RFP-1. His6x-RFP-1 was co-expressed in E. coli with either GST or GST-MRG-1. Immunoprecipitation of GST-MRG-1 also immunoprecipitated His6x-RFP-1, but not by GST alone (top panel). Likewise, using Ni-NTA beads GST-MRG-1 was isolated together with His6x-RFP-1 (second panel). Controls demonstrate that GST, GST-MRG-1 and His6x-RFP-1 were efficiently isolated (third and bottom panels).