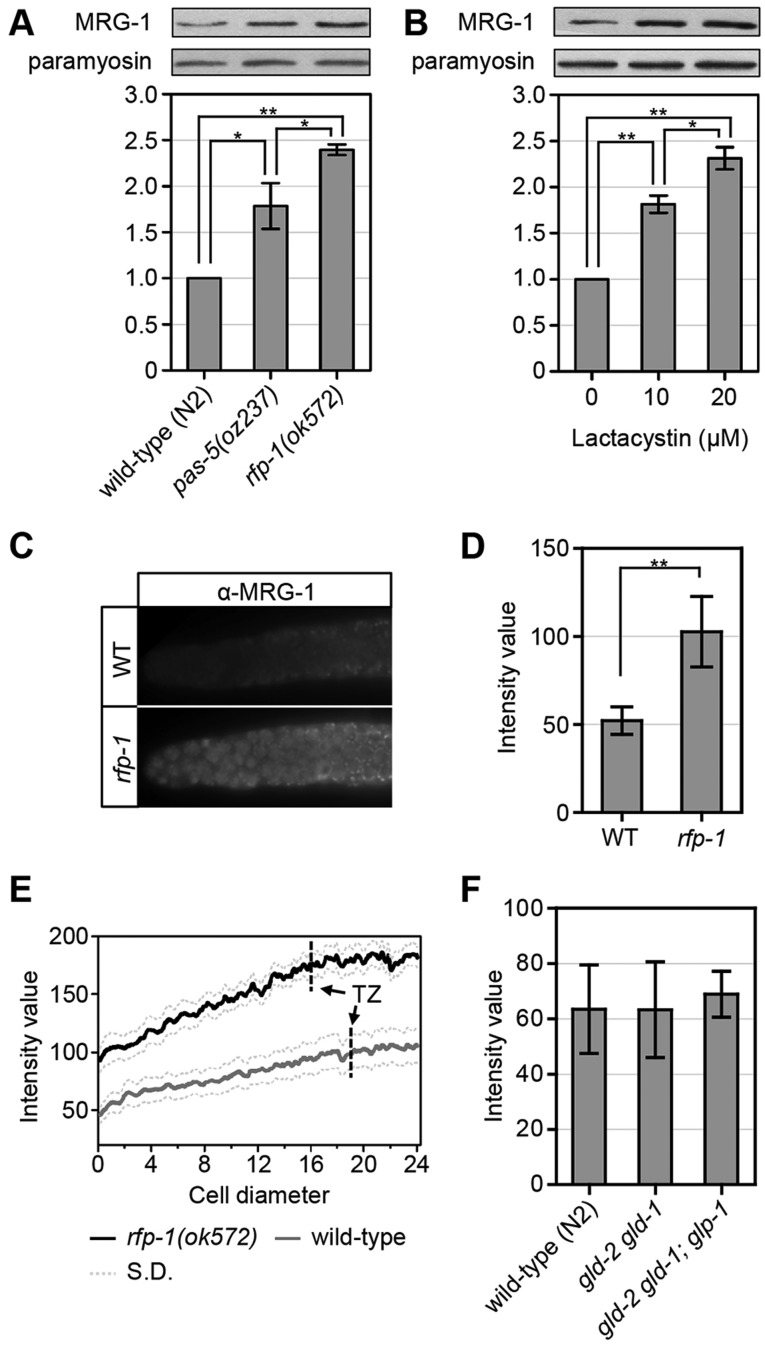
Fig. 7.
MRG-1 level is regulated by the proteasome. (A,B) MRG-1 levels increase when proteasome activity is reduced. (A) MRG-1 levels are higher in pas-5(oz237) and rfp-1(ok572) mutants compared with N2 (wild type). (B) Animals treated with increasing concentrations of lactacystin (proteasome inhibitor) have increasing MRG-1 levels. For both A and B, intensity measurements were averaged from four separate experiments. (C-E) MRG-1 levels are higher in rfp-1(ok572) single mutants. (C) Representative images of wild-type and rfp-1(ok572) gonads immunostained with anti-MRG-1 antibodies. MRG-1 is detected even at the most distal end of the wild-type gonad, but at lower levels than in rfp-1(ok572) mutants (see D and supplementary material Fig. S2). (D) Average MRG-1 intensity is higher in rfp-1(ok572) gonads than in wild type (n=23). (E) Average MRG-1 intensity along the gonad arm from distal end to transition zone (TZ) (n=9). MRG-1 levels are higher in rfp-1(ok572) mutants than in wild type, with lower levels in the distal end than in the transition zone. Dotted lines indicate s.d. In C-E, actual genotypes are unc-32(e189) for wild type and rfp-1(ok572) unc-32(e189) for rfp-1. (F) Average MRG-1 levels are similar in wild-type, gld-2(q497) gld-1(q485) and gld-2(q497) gld-1(q485); glp-1(q175) gonads (n=14). Actual genotypes are unc-32(e189), gld-2(q497) gld-1(q485); unc-32(e189) and gld-2(q497) gld-1(q485); unc-32(e189) glp-1(q175). (A,B,D) *P<0.01, **P<0.001, two-tailed Student's t-test. Error bars indicate s.d.