Fig. 3.
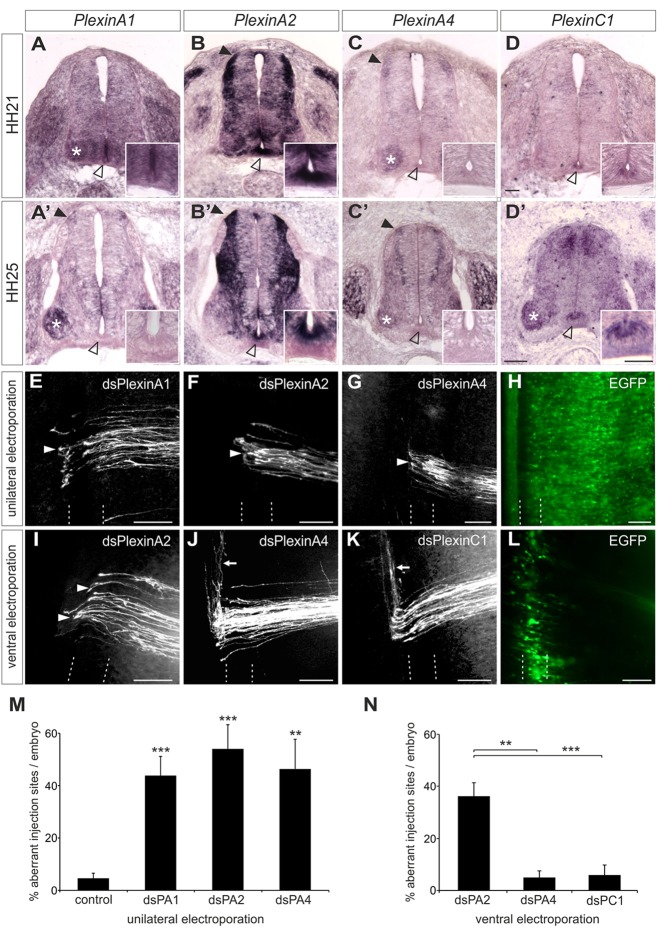
For correct pathfinding, PlxnA2 is required in both commissural neurons and the floorplate. (A-D′) Expression patterns of plexins analyzed by in situ hybridization at stages HH21 (A-D) and HH25 (A′-D′). Staining in commissural neurons is indicated by closed arrowheads. Motoneurons are marked with asterisks. The floorplate is indicated by open arrowheads and shown at higher magnification in the insets. (E-G) After downregulation of PlxnA1 (E), PlxnA2 (F) or PlxnA4 (G) by unilateral electroporation of dsRNA, axons failed to turn rostrally at the contralateral floorplate border (arrowheads). (H) Only injection sites in the electroporated area (verified by EGFP expression) were included in the analysis. (I-K) Analysis of commissural axon pathfinding after downregulation of PlxnA2 (I), PlxnA4 (J) or PlxnC1 (K) exclusively in the ventral spinal cord. After ventral downregulation of PlxnA2 (I, arrowheads), post-crossing axons failed to turn into the longitudinal axis or even turned caudally. Axon guidance was unaffected after ventral downregulation of PlxnA4 (J, arrow) or PlxnC1 (K, arrow). (L) Successful and exclusive targeting of cells at the ventral midline was verified by EGFP expression. The floorplate is indicated by dashed lines. (M,N) Quantification of injection sites with aberrant axonal pathfinding after (M) unilateral or (N) ventral electroporation of dsRNA. ***P<0.001; **P<0.01; error bars indicate s.e.m. Scale bars: 50 μm in A-D′; 100 µm in E-L.