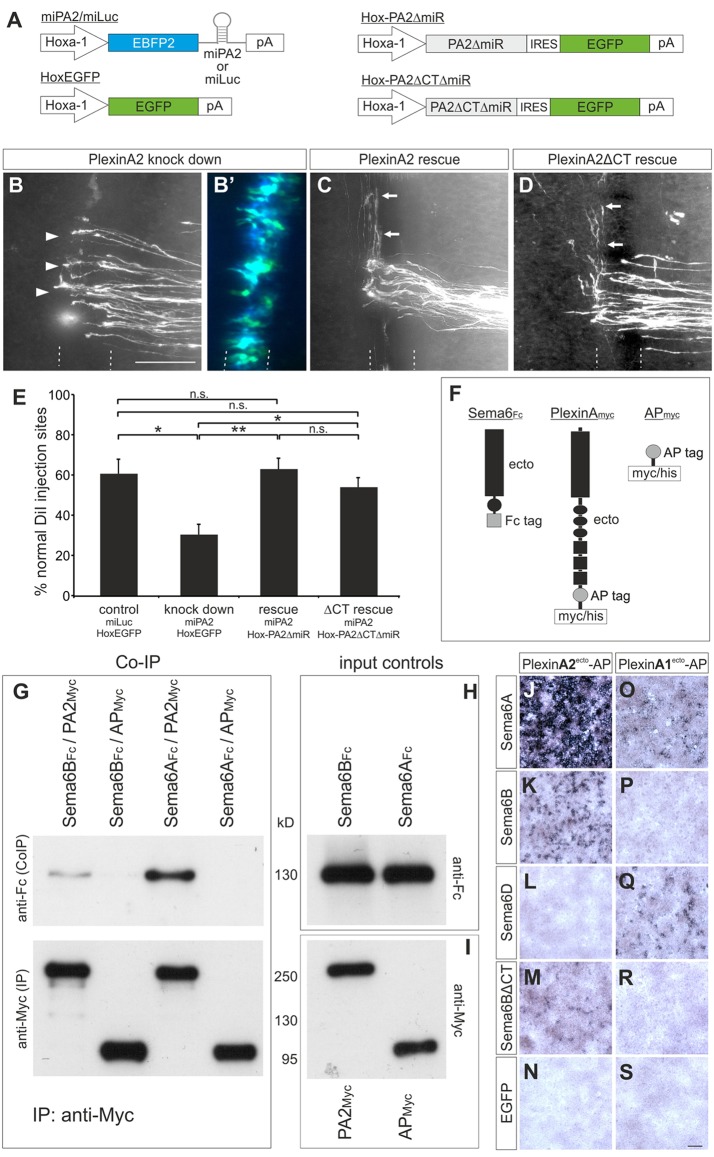
Fig. 4.
The extracellular domain of PlxnA2 mediates its axon guidance activity in the floorplate and binds to Sema6B. (A) Schematics of the constructs used in B-E. Hoxa1 drives floorplate-specific expression. (B-D) Open-book analysis of embryos co-electroporated with: (B) miPA2 and Hox-EGFP; (C) miPA2 and Hox-PA2ΔmiR; or (D) miPA2 and Hox-PA2ΔCTΔmiR. (B′) The successful and exclusive targeting of floorplate cells was confirmed by EGFP and EBFP2 fluorescence from the co-electroporated constructs. Post-crossing axons that failed to turn correctly at the contralateral floorplate border are indicated by arrowheads (B). Arrows (C,D) indicate normal crossing and turning of commissural axons. (E) Quantification of injection sites with normal axon pathfinding after floorplate-specific manipulations of PlxnA2. *P<0.05, **P<0.01; n.s., not significant; error bars indicate s.e.m. (F) Schematics of the proteins used for co-IPs. (G) Sema6BFc or Sema6AFc ectodomains were incubated with either PA2Myc ectodomains or APMyc, and immunoprecipitated with anti-myc agarose beads. Co-IP of Sema6B and Sema6A was detected with anti-Fc antibodies on western blots (upper panel). Blots stained with anti-myc antibodies, to demonstrate the successful immunoprecipitation, are shown below. As controls, the input proteins from conditioned media were analyzed on blots developed with (H) anti-Fc antibodies to detect Sema6BFc and Sema6AFc ectodomains and (I) anti-myc antibodies to detect PA2Myc and APMyc. (J-S) HEK293T cells were transfected with chicken Sema6A (J,O), Sema6B (K,P), Sema6D (L,Q), Sema6BΔCT (M,R) or EGFP (N,S) and incubated with conditioned medium containing AP-tagged ectodomains of PlxnA2 (PlexinA2ecto-AP, J-N) or PlxnA1 (PlexinA1ecto-AP, O-S). Scale bars: 100 μm.