Fig. 1.
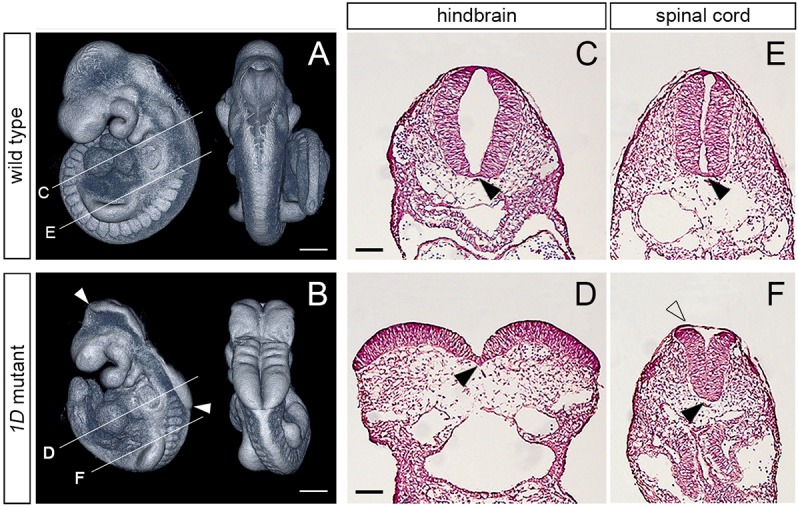
The 1D mutation causes exencephaly and spinal cord defects. (A,B) Lateral (left) and dorsal (right) views of E9.5 wild-type and 1D mutant embryos obtained from micro computed tomography (microCT) scans. Arrowheads in B demarcate the extent of exencephaly in the 1D mutant. Lines indicate the level of cross-sections shown in C-F. (C-F) Cross sections through the hindbrain (C,D) and spinal cord (E,F) regions in E9.5 wild type and 1D mutants. Black arrowheads point to the medial hinge point. Unfilled arrowhead in F points to the surface epithelia covering the abnormally shaped neuroepithelia in 1D embryos. Scale bars: 300 µm (A,B); 100 µm (C-F).
