Fig. 2.
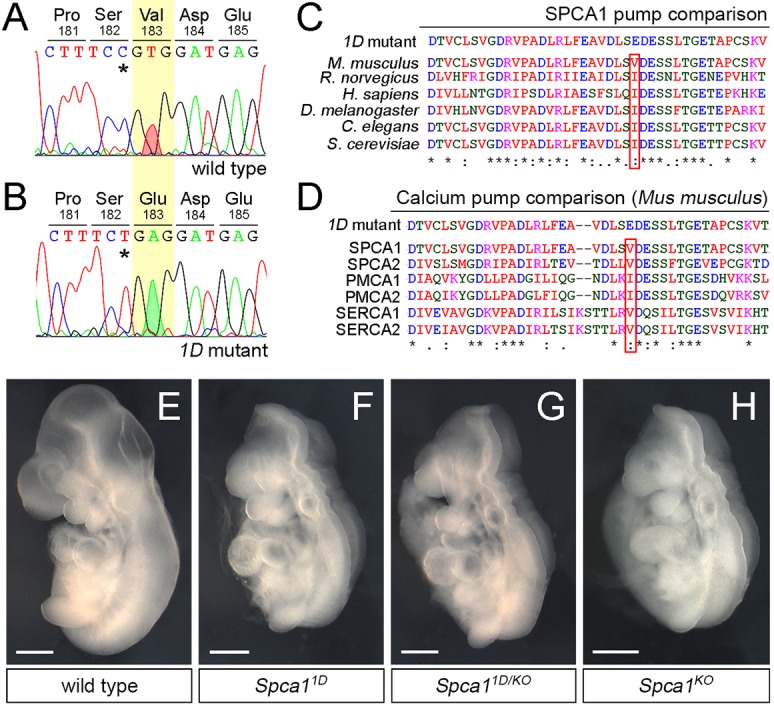
1D mutants contain a non-conservative mutation in SPCA1. (A,B) Sanger sequencing traces for the Spca1 coding region in wild type and 1D mutants. 1D embryos contain a T-to-A nucleotide difference (red and green shaded peaks), which is predicted to cause a Val-to-Glu amino acid change at position 183 (highlighted in yellow). Residue numbers are based on NP_778190 sequence. Note that the Spca1 sequence shown contains a known silent polymorphism between the FvB (wild-type) and C57J/B6 (1D mutant) strains (C-T SNP, asterisks). (C,D) Protein sequence alignments showing the conserved nature of the mouse SPCA1 V183 residue across species (C) and in comparison with other mouse Ca2+ ATPases (D). Conservation is indicated for identical residues (asterisks), for residues with strong similar properties (double dot) and for residues with weakly similar properties (dot). SPCA2, PMCA1, PMCA2, SERCA1 and SERCA2 are also known as ATP2C2, ATP2B1, ATP2B2, ATP2A1 and ATP2A2, respectively. (E-H) Lateral views of E9.5 wild-type (E), Spca11D homozygotes (F), Spca11D/KO trans heterozygote (G) and homozygote Spca1KO (H) embryos. Scale bars: 500 µm.
