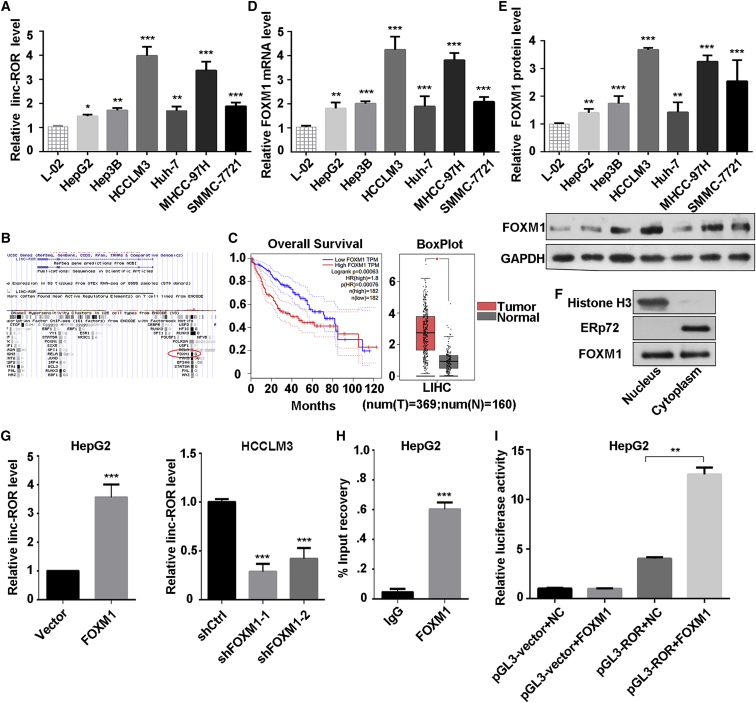
Figure 1.
LINC-ROR Was Upregulated in HCC Cells and Activated by FOXM1
(A) The expression level of LINC-ROR in a normal liver cell line and six HCC cell lines were tested by quantitative real-time PCR. (B) The binding region of FOXM1 at the promoter of LINC-ROR in the UCSC Genome Browser (assembly >hg19, DNA range: chr18:54,745,025–54,745,392; strand, +). (C) The overall survival curve in HCC patients with high or low FOXM1 expression and a boxplot analysis of FOXM1 expression in normal and tumor tissues are shown, based on GEPIA data (http://gepia.cancer-pku.cn/). (D) The expression level of FOXM1 mRNA in a normal liver cell line and six HCC cell lines was tested by quantitative real-time PCR. (E) Western blot analysis of the protein level of FOXM1 in a normal liver cell line and six HCC cell lines (bottom) and the quantification of FOXM1 protein (top). (F) Relative enrichment of FOXM1 proteins in purified nuclear and cytoplasmic fraction by nuclear and cytoplasmic protein extraction assay. Histone 3 was used as the nuclear marker, and ERp72 was used as the cytoplasmic marker. (G) LINC-ROR expression was measured by quantitative real-time PCR in HepG2 or HCCLM3 cells transfected with FOXM1, shFOXM1-1, or shFOXM1-2, with relative control groups. (H) ChIP assays using anti-FOXM1 or anti-IgG antibody were applied to determine the affinity of FOXM1 on LINC-ROR promoter in HepG2 cells. Relative enrichment is normalized to IgG as the negative control. (I) Dual-luciferase reporter assays were performed to confirm the binding of FOXM1 and the LINC-ROR promoter in HepG2 cells. All data are presented as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. The p values represent comparisons between groups (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001).